Introduction
In the world of industrial automation, processing data in real-time at the edge of the network is becoming increasingly important. IIoT Edge Gateways equipped with built-in algorithms for edge analysis and onboard data processing are revolutionizing how industries operate. This blog explores the significance of these capabilities, the benefits they offer, and real-world applications.
What is Edge Analysis?
Edge analysis refers to the processing of data at the edge of the network, close to where the data is generated. Unlike traditional cloud-based analysis, edge analysis allows for immediate data processing and decision-making, reducing latency and providing real-time insights.
Difference Between Edge Analysis and Cloud-Based Analysis
Beneficial Features for Edge Analysis
Reduced Latency:
By processing data locally, edge analysis minimizes the delay between data generation and actionable insights, enabling immediate decision-making.
Real-time Insights:
It will analyze data as it is generated, providing instantaneous insights and allowing for prompt responses to any anomalies or changes.
Enhanced Security:
Local data processing reduces the exposure of sensitive data, minimizing the risk of cyber threats and data breaches.
Lower Bandwidth Usage:
Since data is processed at the edge, only relevant and summarized information is transmitted to the cloud, reducing overall bandwidth requirements.
Reduced Cost:
Cloud computation is relatively expensive. With Edge Analysis,, you can reduce the cost of operations by reducing the cost of cloud charges.
Key Use Cases
Data Cleaning:
Raw data is segregated and cleaned thoroughly. Data garbage, such as interesting and outliers, is removed.
Data Aggregation:
Data is aggregated & summarised at the granule level. Aggregation such as sum, multiplication, scaling, and statistical computations are performed. A custom aggregate code can also be interesting.
Relation-based Computation:
Many of the formulas that depend on multiple data points can also be integrated.
Predictive Maintenance:
A built-in formula can predict equipment failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
Real-time Quality Control:
Continuous monitoring of production quality in real-time ensures that defects are detected and addressed immediately.
Energy Management:
Optimize energy usage across operations, reducing costs and improving sustainability.
Anomaly Detection:
Detects abnormal patterns in data that may indicate potential issues, enabling proactive measures.
How Built-in Algorithms Work
- Data Collection: The IIoT Gateway collects data from various sensors and devices within the industrial environment.
- Data Preprocessing: The collected data is cleaned and organized for analysis, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Algorithm Execution: Machine learning and statistics formulas are executed on the edge device to analyze the data and generate insights.
- Actionable Outputs: The analysis results are used to generate actionable insights and automated actions, such as triggering maintenance alerts or adjusting operational parameters.
Examples of Integrated Formula
Category 1: Predictive Maintenance
Failure Prediction: Identifies patterns that indicate an impending failure.
Remaining Useful Life Estimation: Estimates the remaining operational life of equipment.
Condition-Based Monitoring: Continuously monitors equipment condition and performance.
Category 2: Quality Control
Defect Detection: Identifies defects in products during the manufacturing process.
Process Optimization: Optimizes manufacturing processes for improved efficiency and quality.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitors process stability and variability using statistical methods.
Category 3: Operational Efficiency
Energy Usage Optimization: Analyzes and optimizes energy consumption.
Anomaly Detection: Detects unusual patterns that may indicate potential issues.
Asset Utilization Tracking: Monitors and optimizes the utilization of assets.
Throughput Analysis: Analyze the production throughput to identify bottlenecks.
Downtime Analysis: Identifies and analyzes the causes of equipment downtime.
Adding Counters: Tracks specific events or conditions over time.
Timers: Measures the duration of specific events or operations.
Multi-tag Validation: Validates the conditions of multiple data points simultaneously.
Multi-tag Mathematical Calculations: Performs complex calculations using multiple data points.
Comparison: Edge vs. Cloud Processing
| Aspect | Edge Processing | Cloud Processing |
| Latency | Lower latency due to local data processing | Higher latency due to data transmission to the cloud |
| Bandwidth | Reduced bandwidth usage | Higher bandwidth usage |
| Security | Enhanced security by keeping data local | Increased exposure due to data transmission |
| Scalability | Limited by the edge device’s capabilities | High scalability for large-scale data storage |
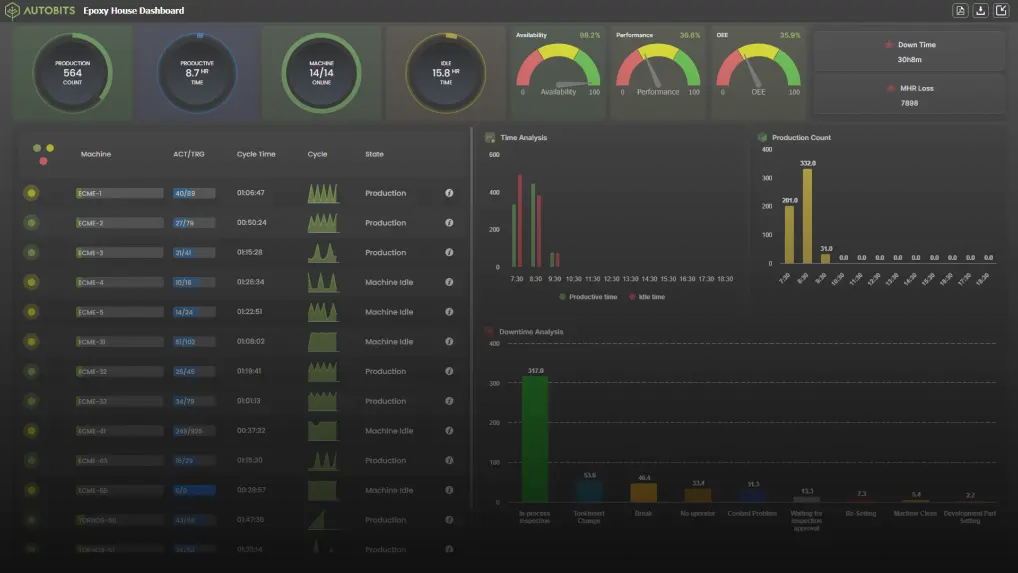
Case Study: Smart Supervisor IIoT Edge Gateway
Scenario: A leading manufacturing plant needed a solution to monitor and optimize their machine assets remotely. Traditional methods were inefficient and led to significant downtimes.
Solution: By integrating the Smart Supervisor IIoT Edge Gateway for edge analysis, the plant achieved real-time data collection and remote diagnostics. This enabled them to:
- Monitor machine health continuously.
- Receive instant alerts for any anomalies.
- Optimize machine performance remotely.
Outcome: The plant saw a 30% reduction in maintenance costs and a 25% increase in operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Built-in accurate formulas for edge analysis and onboard data processing in IIoT Edge Gateways are transforming industrial operations. By providing real-time insights, reducing latency, and enhancing security, these capabilities are essential for modern industrial automation. Embrace the future of industrial automation with IIoT Edge Gateways equipped with advanced.
Ready to enhance your industrial operations with edge analysis and onboard data processing? Contact Autobits today to learn more about our IIoT Edge Gateway solutions and how they can benefit your operations.