Manufacturing is changing fast. Many teams want to know how Industry 4.0 is different from Industry 5.0. Both terms look similar, but they are not the same. This guide explains everything clearly.
Industry 4.0 brought intelligent machines and real-time data. Industry 5.0 focuses on people, personalisation, and better use of technology. When you understand both, it becomes easier to plan what your factory needs next.
What you will learn in this guide
You will learn what Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 mean. You will see how Industry 1.0 to 5.0 evolved. You will learn the key features, benefits, and challenges of each stage. You will also learn simple steps to prepare your factory for Industry 5.0.
Industry 1.0 to 5.0: A quick timeline
Industry 1.0 (late 1700s) Steam-driven mechanisation
The first industrial shift replaced craft workshops with steam-powered machines. Small factories appeared, and productivity increased compared to hand-made goods. For manufacturers today, this era matters because it started the idea of applying technology to scale production.
Industry 2.0 (late 1800s to early 1900s) Electricity and mass production
Electric power and assembly line thinking made mass production practical and affordable. Standardised parts and repeatable processes became the norm. Many modern shop floor principles trace back to this period.
Industry 3.0 (late 1900s): Automation and electronics
Computers and programmable controllers introduced automated control and repeatability to manufacturing. This is where PLCs and basic shop floor automation became common. If you run CNC machines today, you are benefiting directly from developments in this era.
Industry 4.0 (2010s onward) Smart factories and connectivity
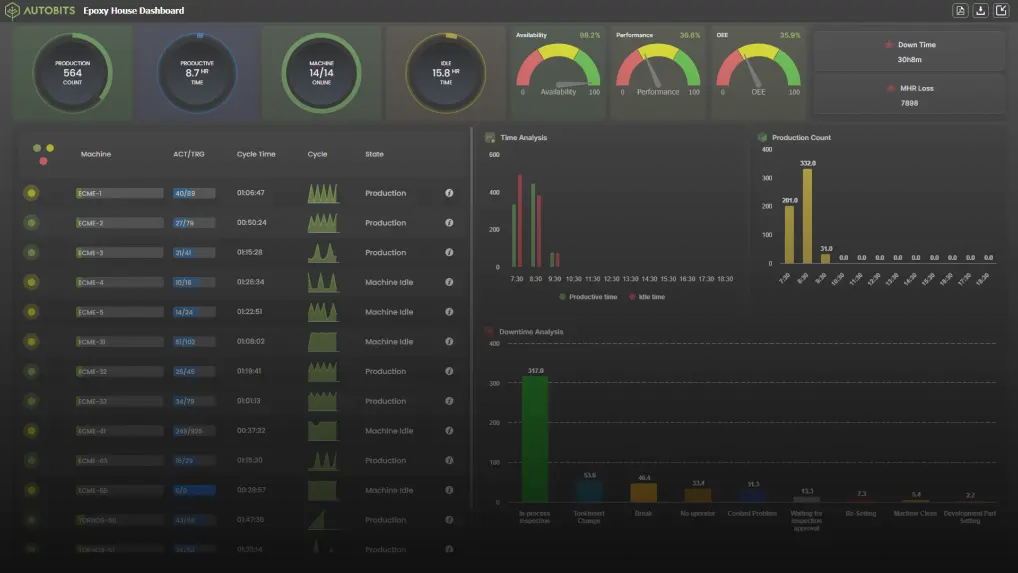
Industry 4.0 added sensors, connectivity, and real-time data to factories. Machines started talking to systems and to people. Concepts such as IoT and cyber-physical systems enabled remote monitoring and data-driven decision-making. For a practical starting point, see our CNC machine monitoring guide and learn how to make shop floors visible with simple sensors.
Industry 5.0 (emerging) Human-centric, personalised, and sustainable production
Industry 5.0 builds on the smart factory but places people, personalisation, and sustainability at the center. The focus shifts to augmenting human skills with collaborative robots and AI, enabling you to offer customised products while reducing waste. If you want to see this in action, explore our Autobits IIoT Gateway and related case studies to understand how human-centric workflows meet connected machines.
Keep the timeline visual for readers. A simple horizontal table or timeline image makes this quick to scan and increases time on the page. Add a small call to action under this section linking to your solutions and case studies so readers can move from history to practical implementation.
Definition of Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0
Picture a factory where humans and robots collaborate side-by-side to leverage both human creativity and machine precision to produce sustainable, low-carbon products for optimized customers. This is the vision of Industry 5.0, the newest evolution of industrial transformation. But what actually differentiates it from Industry 4.0, the intelligent automation revolution? This blog will identify the important features, technological advancements, positives, and pitfalls of transforming into Industry 5.0, offering insight for both businesses and practitioners.
What Are Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0?
Industry 4.0 is also known as the 4th Industrial Revolution. Industry 4.0 introduced intelligent automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Big Data to manufacturing. The primary technique for Industry 4.0 is interconnectivity of systems in a traceable manner to achieve greater efficiency, less human interaction, and reduce redundancies in production. For example, under the context of Industry 4.0, real-time condition monitoring of factory equipment implies the use of IoT sensors to track and estimate output and be aware of downtime.
Industry 5.0 is based on the advancements of Industry 4.0 but pivots toward creating innovative systems that value the human factor in the industry. Specifically, Industry 5.0 emphasizes the collaboration tool between humans and advanced technologies, such as AI and robots to establish sustainable, flexible and personalized manufacturing systems. While Industry 4.0 prioritizes automation, Industry 5.0 permits workers to utilize their creativity, experience, ethical judgment, and problem-solving skills. The emphasis and symbiosis between worker creativity and their productivity creates greater motivation and satisfaction at work.
Industry 5.0 vs Industry 4.0: Key Differences
The following table highlights the core differences between Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0, focusing on their approach to technology, human roles, and goals:
| Aspect | Industry 4.0 | Industry 5.0 |
| Core Focus | Full automation and data-driven processes to maximize efficiency. | Human-machine collaboration for flexibility, customization, and sustainability. |
| Human Role | Minimal human involvement; humans monitor automated systems. | Humans and machines work together, leveraging creativity and precision. |
| Automation Approach | Heavy reliance on robotic systems, e.g., automated assembly lines in car manufacturing. | Use of collaborative robots (cobots), e.g., BMW’s cobots assist workers in assembling customized parts. |
| Customization | Limited to standardized mass production with some flexibility. | High customization, e.g., Adidas uses AI and human oversight for custom sneakers. |
| Sustainability | Limited focus on eco-friendly practices. | Prioritizes sustainable processes, e.g., Tesla’s energy-efficient battery production. |
| Example Outcome | Faster production with reduced costs through automation. | Personalized, high-quality products with reduced environmental impact. |
This human-centric focus in Industry 5.0 enables more adaptive, creative, and sustainable manufacturing compared to Industry 4.0’s automation-driven model.
Technological Advancements Driving the Transition
Industry 5.0 leverages and refines Industry 4.0 technologies to create a more collaborative and intelligent ecosystem.
Automation & Collaborative Robots
In Industry 4.0, automation exploited the potential of robotics and deployed widespread automation, consisting of robotic arms making products from part to part with little human input. Industry 5.0 refines this vision by bringing in collaborative robots or “cobots” designed explicitly to work with humans in any environment. Cobots, for example, are employed by Siemens in electronics manufacturing to aid with tedious tasks like pin point soldering, which frees humans to do the fun creative consideration with more encouragement and it enhances flexibility and ultimately mass customization.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The use of AI in Industry 4.0 is largely centered on automating decisions to provide decision support (e.g. predictive maintenance alerts to ensure failures don’t occur). AI in Industry 5.0 enables human aided decision making and represents the emergence of different systems of adaptive learning that learn from multiple human inputs. In this example AI, could suggest different product designs based on analysis of customer preferences, and humans could coordinate the output.
Connectivity & Intelligent Networks
Industry 4.0 utilized a combination of IoT and sensors to assess connectivity to facilitate real-time monitoring capabilities to manage stock levels in on hand inventory, and data traceability. Industry 5.0 introduces additional possibilities that include edge computing to facilitate data processing in close proximity to the data sources to gain faster reactivity and engage localized next-generation networks connected (e.g. 6G), for ultra-high speed and reliable communication. This convergence intersects on a global collaborative platform to enable engineers to co-design connected product from multiple continents in real time.
Read: The Power of Real-time Production Monitoring Software: Beyond Just Counting Parts
Benefits of Transitioning to Industry 5.0
The shift to Industry 5.0 offers significant advantages:
Greater Efficiency and Productivity
Industry 5.0, by integrating human intuition with AI sophistication, minimizes errors and enhances production. For example, cobots execute repetitive tasks, allowing workers to focus on quality control which leads to less defects and lower costs.
Greater Product Personalization
Industry 5.0 allows for a product to be highly personalized, while still being efficient. For instance, Adidas utilizes principles from Industry 5.0 to make custom sneakers, with AI optimizing designs, and humans controlling quality to deliver quicker to customers.
Sustainability and Ethical Production
Industry 5.0 is a set of principles that allow companies to put sustainability first, like using energy-efficient machines, or implementing processes that reduce levels of waste. Some companies, like Tesla, utilize human-AI collaboration to produce batteries and improve car batteries in a sustainable manner.
Global Connectivity
Networks and advances in technology allow production systems to be decentralized without borders, meeting the demand in real-time across the globe. This represents a paradigm shift in the supply chain that can lead to increased agility and resiliency. For example, pharmaceutical companies executed global coordinated vaccine production during a pandemic that improved global preparedness.

Challenges of Adopting Industry 5.0
While promising, the transition to Industry 5.0 comes with hurdles:
- Costs: The implementation of cobots, artificial intelligence, and 6G infrastructure may be sizable. Small businesses might not be able to afford these upgrades.
- Reskilling the Workforce: The workforce will need training in order to work with advanced technologies; this training takes time and cost money. For example, operators will need to learn how to implement programming and maintenance of cobots.
- Cybersecurity: Greater connectivity like 6G and, simultaneously, edge computing will bring more cyber-attacks and consequently require more robust security measures.
- Ethical considerations: Problems related to AI will become more pronounced if we create reliance on AI; this could involve large questions about displacement of jobs or transparent decision making, and require the development of ethical frameworks.
How to Prepare for Industry 5.0
To embrace Industry 5.0, businesses and professionals can take these steps:
- Focus on Training: Upskill workers on AI, robotics, and data analysis using resources like Coursera or industry-specific workshops.
- Use Modular Technologies: Adopt scalable solutions first starting with cobots or cloud-on-boarding (e.g. cloud-based AI).This will ease the transition to Industry 5.0.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity: Use encryption and regular audits for connected systems, and cybersecurity plans for your robots.
- Embrace Sustainability: Connect machines that are energy-efficient in design and employ circular production models to evolve with the deep ethos of Industry 5.0.
- Promote Teaming: Break team boundaries to bring together necessary skills (both technical and creative) to enhance human-machine partnerships and collaboration.
Industry 5.0 Beyond Manufacturing
While manufacturing leads the way, Industry 5.0 principles apply to other sectors:
- Healthcare: AI-assisted diagnostics, like IBM Watson, help doctors personalize treatments, with human oversight ensuring accuracy.
- Logistics: Companies like DHL use cobots to optimize warehouse operations, with workers handling complex decision-making.
- Finance: AI-driven fraud detection systems work with human analysts to ensure ethical compliance.
Conclusion
Industry 5.0 is a transformation away from the automated Industry 4.0 to a future where humans and machines work in harmony for better, greener, and personalized production. By adopting new technologies like collaborative robots, AI, and industry 4.0 networks, companies can achieve new levels of efficiency and creativity while tackling complex challenges such as costs and retraining. Are you able to explore industry 5.0? Start with training and sustainable technologies to get ahead in this human-centric revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Industry 4.0 & Industry 5.0
What exactly is Industry 5.0?
Industry 5.0 represents the next advancement in the evolution of industry and centers specifically on the collaboration of humans and machines. Industry 5.0 seeks to incorporate artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and robotics along with human knowledge, expertise, and workflows in order to create a sustainable, efficient, and effective production environment.
How does Industry 5.0 differ from Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is focused on fully automated processes using data-driven decisions. Industry 5.0 focuses instead on the collaboration of humans and machines working together, while also focusing on additional factors such as personalization, creativity, and sustainability of processes.
What are the top benefits of Industry 5.0?
The top benefits of Industry 5.0 include greater efficiency, improved product quality, better human-AI collaboration, new sustainable processes, and increased access and utilization with intelligent networks.
How will Industry 5.0 change job opportunities?
Industry 5.0 will not take away jobs, but it will change jobs. It will create more job opportunities requiring human expertise for AI training using data from mass customization, decision making, and ethical advisory roles to ensure workforce and workforce opportunities to skill humans to get involved.
Is Industry 5.0 only for the manufacturing industry?
No, while manufacturing is indeed probably the key industry, the principles of Industry 5.0 can be applied in many industries, such as healthcare, finance, logistics, or other industries where human-AI collaboration can lead to more effective utilization and/or networking of knowledge. Industry 5.0 marks the time when technology and human intelligence create a successful partnership for industrial innovation, while still trying to enhance the industrial environment in a sustainable way to improve the user experience.