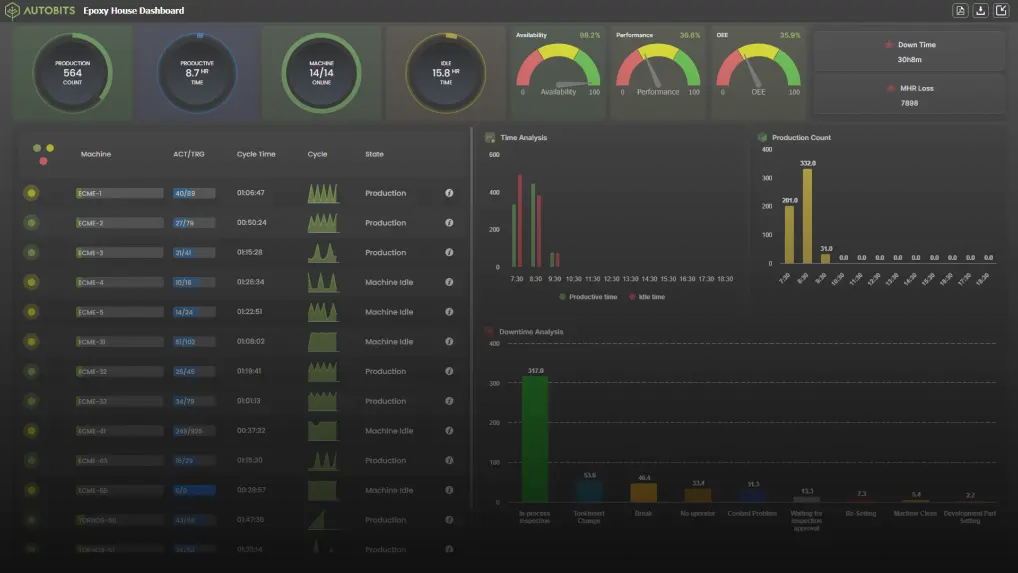
IoT has a pretty straightforward role in fleet management. Sensors and devices are embedded in the vehicles. Data are then captured and analyzed which may trigger alerts and notifications. It is mostly used to track:
IoT has a pretty straightforward role in fleet management. Sensors and devices are embedded in the vehicles. Data are then captured and analyzed which may trigger alerts and notifications. It is mostly used to track:
Driver Behavior:
Ad-on, third party sensors are attached to the vehicle along with traditional GPS technology to not only track physical location but also monitor driving habits.
Fuel efficiency:
The fleet manager always wants to target on increasing the efficiency while cutting the cost. And one of the most crucial factor here is the efficiency of fuel. It is important to know how the behavior of driver affects fuel efficiency. Events like how long the trucks are idling, how fast the vehicles are going on average on top of the actual consumption data, how quickly they are being accelerated and decelerated. Depending on the model of the truck, fuel efficiency can be tracked by both retrofitted and embedded sensors.
Maintenance:
When monitored parts are close to failure or are in need of a tune up, signals can be sent from the sensors embedded to the vehicle. Sensors can be used to monitor tire’s pressure level, allowing the driver to inform about the wear out before its too late.
In late 2013, there were around 11 million fleet management connected devices which is forecasted to increase to 60 million. Connected fleet has many benefits. Connected ships accelerates productivity and efficiency. It gets a hold on increasing environmental disturbance.
They also help improve the operational efficiency. According to stats, there is:
- 15% increase in vehicle efficiency
- 15% reduction in material waste and cost
- 25% reduction in accidents and injuries
- 50% increase in labor productivity
- 68% reduction in vehicles travelling to site
Smart fleet management helps reduce environmental impact to a great extent. It can reduce fuel consumption, emissions and also minimize carbon footprint layers. If used efficiently, it can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 75% and reduce fuel consumption by 26%.