NC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are changing the face of modern manufacturing by providing precision, efficiency, and automation. But how does a CNC machines work? In this guide, we will break down the process step-by-step from programming to action so you understand how the machines produce the digital formats into life.
What is a CNC Machine?
A CNC machine is an automated manufacturing tool controlled by a computer. It precisely follows programmed instructions to cut, shape, and assemble materials with extreme accuracy.
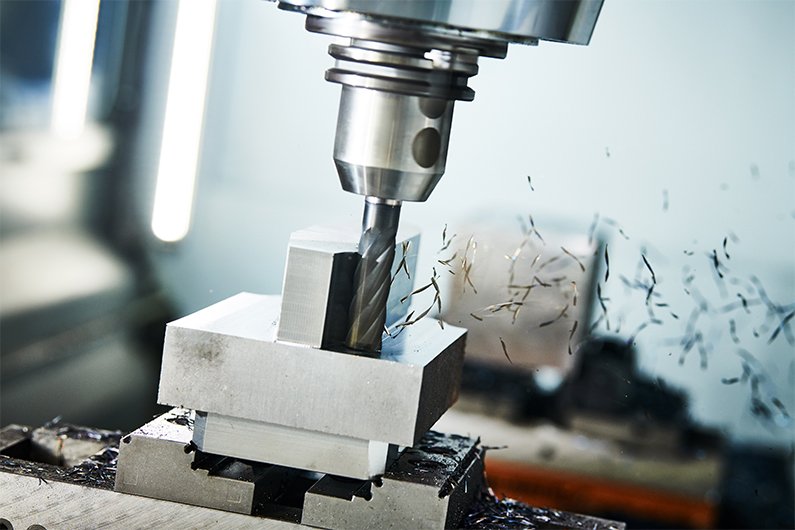

Types of CNC Machines
It come in various forms, such as:
- CNC Milling Machines – Used for cutting and drilling materials.
- CNC Lathes – Designed for rotating parts and cutting.
- CNC Routers – Used for engraving, cutting, and shaping wood, plastic, and metal.
- CNC Plasma Cutters – Utilize plasma torches to cut metals.
- CNC Laser Cutters – Provide high-precision laser cutting.
- CNC 3D Printers – Use additive manufacturing techniques.
How CNC Machines Work
The Role of CAD and CAM Software
The cycle of CNC begins with a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) program. Designers create a 2D or 3D digital representation of the part. This design is then translated into machine-readable code through Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software.
Programming the CNC Machine
CNC machines use a special programming language called G-code, which provides instructions such as:
- Movement (X, Y, Z coordinates)
- Cutting speed
- Tool changes
- Depth of cuts
Setting Up the Machine
Before starting, the operator:
- Mounts the material (wood, metal, plastic, etc.)
- Loads the required tools (drill bits, cutting blades, etc.)
- Aligns and secures everything properly to ensure accuracy
The Machining Process
Once the program is uploaded, the CNC machine automatically executes the following steps:
- Material Positioning – The workpiece is securely placed.
- Tool Movement – The cutting tool moves according to G-code instructions.
- Precision Cutting – The machine removes material layer by layer to create the desired shape.
- Cooling and Lubrication – To prevent overheating, CNC machines use coolants.
- Quality Inspection – Sensors or operators inspect the final product for accuracy.
Automation and Repeatability
CNC machines can perform the same task with zero variation, making them perfect for mass production. Once a program is set, it can be repeated indefinitely with the same level of precision.
Post-Processing and Finishing
After machining, the part may require finishing processes like polishing, painting, or heat treatment to enhance durability and aesthetics.
How to Operate a CNC Machine
Operating a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine requires an understanding of the hardware and software used to control a CNC automated machining process. There is technical knowledge of the machine required, setup of the machine, plus safety considerations when working with the equipment. Whether the machining operation involves milling, turning or drilling, approaching the task with a step-by-step process, is critical for accuracy, productivity, and safety.
Steps to operate a CNC machine:
- Prepare the machine: Power on the CNC machine and execute the necessary checks (coolant levels, tool alignment, etc.).
- Load the workpiece: Secure the raw material on the machine bed or fixture securely.
- Set up the tooling: Install the required cutting tools in the spindle or turret.
- Upload the CNC program: Load the G-code (by USB, network, or control panel).
- Set work offsets: Define the machine’s zero position using the control panel (usually X, Y, Z axes).
- Run a dry test: Execute the program without cutting to check for errors.
- Start the operation: Start machining, but ensure it’s supervised properly.
- Monitor and make adjustments: Observe the process and be prepared to make feed, speed, or tooling changes as necessary.
- Finish and clean up: When the job is finished remove the part, inspect it, and clean the machine itself.
Make sure you follow safety protocols, wear the required protective gear, and have appropriate training before operating a CNC machine.
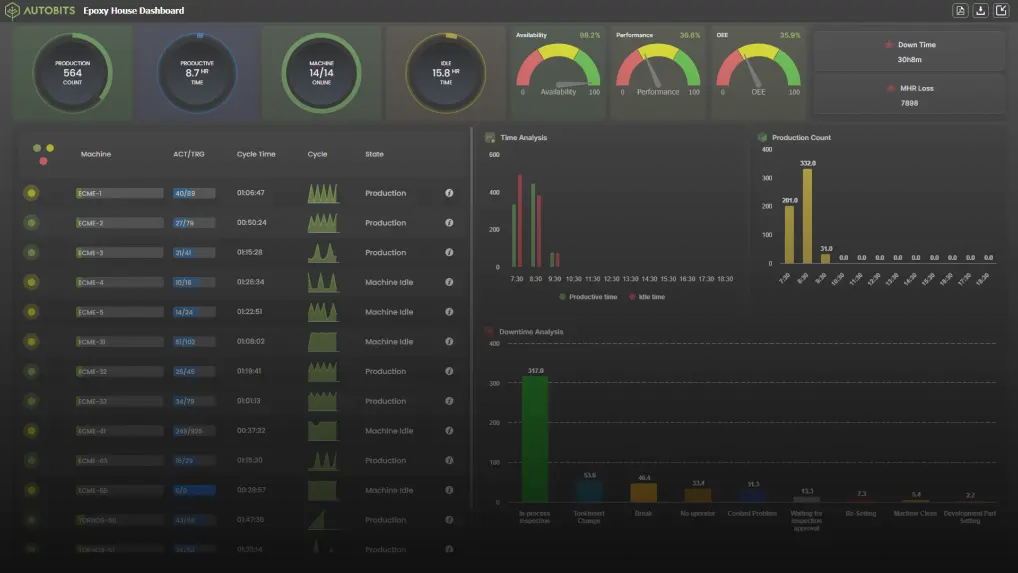
Top CNC Machine Monitoring Software in the USA – Boost Efficiency & Productivity
Discover the best CNC machine monitoring software in USA to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and increase operational efficiency. Explore features, benefits, and top solutions optimized for manufacturers.
Conclusion
CNC machines have changed industries, offering unparalleled precision, automation, and efficiency. From creating designs in CAD software to performing exact cuts and machining operations using G-code programming, CNC machines are a vital part of the manufacturing process. CNC technology provides a high-quality outcome, whether being used on a prototype or at-scale production with little human intervention.
FAQs about CNC Machines & How It Works
Which industries utilize CNC machines, and how are they used in each industry?
CNC machines are used in the aerospace, automotive, medical, construction and consumer goods industries for manufacturing high precision parts.
In what materials can CNC machines cut and shape?
CNC machines can cut and shape metals, plastics, wood, foam and even composite materials such as carbon fiber.
What is the difference between G-code and M-code?
G-code controls the movement and operation of the machine while M-code instructs the machine for auxiliary functions such as turning the spindle on and off or changing tools.
What degree of accuracy do CNC machines have?
CNC machines can have an accuracy of within .001 making them separated in precision.
Can CNC machines be commonly used for small businesses?
Yes! Many small businesses commonly use CNC routers and mills for custom fabrication, engraving and prototype development.