Introduction
Industry 4.0, often known as the fourth industrial revolution, marks a significant transition in modern industry. It combines modern digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and automation to build “smart factories” in which machines, systems, and processes interact and communicate seamlessly.
Industry 4.0 makes production more efficient, accurate, and flexible by harnessing these technologies. This progress in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine operations has resulted in improved communication, real-time data monitoring, and autonomous decision-making, revolutionizing how industrial processes are managed and optimized.
A Brief Overview of Industry 4.0 in Modern Manufacturing
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, represents a dramatic transformation in how manufacturing processes are carried out by combining modern technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), Machine learning (ML), and Big Data analytics.
Some of the primary features of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing
- Automation and smart systems
- Data-Driven Decision Making
- Customization and Flexibility
- Interconnectivity
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
- Predictive Maintenance and Efficiency
Understanding Industry 4.0 and its Core Technologies
Industry 4.0 Overview
Industry 4.0, often known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the continuing period in which automation and digitalization have dominated the industrial industry. It refers to the integration of numerous advanced technologies that are changing the way individuals and businesses work.
Industry 4.0 aims to develop smart factories that are modern and digitally advanced industrial facilities. They use networked devices, equipment, and systems that constantly collect and exchange data with one another via sensors, advanced data analytics, and machine learning algorithms.
Core technology: AI, IoT, Big Data, Machine Learning, and Cloud Computing
AI
When artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) interact, it’s as if they’re building a super-smart system capable of handling massive amounts of data in real-time, predicting what might happen next, and increasing overall efficiency. As more devices connect to the internet via IoT, they generate massive amounts of data.
IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of devices or items that are linked together via an Internet connection. IoT refers to the linking of various devices to the Internet. These devices may include several appliances that must be connected for purposes such as automation and real-time device control.
Big data
Big Data refers to the process of analyzing enormous amounts of structured and unstructured data to get insight into various business processes. Big Data refers to data that is too huge or complex to process using traditional methods.
Cloud computing
The Cloud is a centralized system that helps in the delivery and transportation of data and various files to data centers via the Internet. The Cloud system offers easy access to various data and software. Cloud computing is a cost-effective alternative because it does not require on-premises infrastructure for storage, processing, and analytics.
Machine Learning
Machine learning enables a system to learn independently from previous data. The idea is to create machines that can learn from data and produce more accurate results. To create prediction models, machine learning techniques are used. ML systems use statistical models to learn and can self-correct when given fresh data.
Industry 4.0 Impact on the Operation of CNC Machines
Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
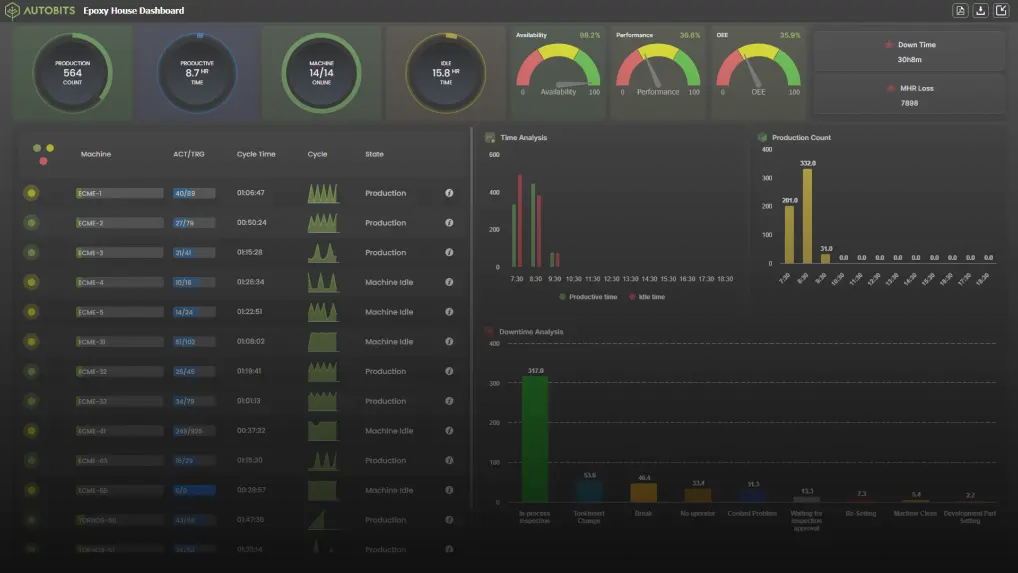
Predictive maintenance is a significant advancement made by Industry 4.0 for CNC manufacturing. Using data from machine sensors and IoT devices may predict difficulties and breakdowns, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. This data improves decision-making, quality control, predictive maintenance, and process optimization, leading to greater productivity and efficiency.
Data analytics also creates opportunities for predictive capabilities, enabling companies to plan and react to market developments and client requests.
Enhanced Automation and Connectivity
Industry 4.0 has significantly impacted CNC production through increased automation and connectivity. IoT and sensor technology have enabled smart CNC machines to connect with humans, allowing for real-time monitoring and management of industrial operations.
In Industry 4.0, CNC machines are integrated into a network of interacting sensors, devices, and systems. That connectivity implies real-time data sharing and feedback, resulting in efficient changes and optimization.
Improved Data Collection and Analysis
Big Data and advanced analytics are revolutionizing CNC manufacturers’ data collection, processing, and utilization, enabling Industry 4.0. Advanced technologies would allow manufacturers to collect and analyze large amounts of data from various sources, including machine sensors and IoT devices.
Advanced Automation and Autonomous Operations
Industry 4.0 allows for predictive maintenance by continuously analyzing data from CNC machines to detect wear and tear or probable breakdowns before they cause downtime. Companies that foresee maintenance needs can schedule repairs at more convenient times, reducing unexpected breakdowns and increasing machine life.
Predictive maintenance lowers repair costs and optimizes the use of tools and components, making operations more cost-efficient.
The Importance of IoT for CNC Machines
Manufacturers who use advanced technologies such as IoT should expect a 20% improvement in productivity. Manufacturers may achieve considerable benefits through integrating sensors, data analysis, and automation into CNC machines. CNC machines are already extremely accurate and productive. Yet, the integration of IoT makes them much more advanced and efficient.
Improved Quality Control
The chance for error is extremely reduced in the highly accurate sector of CNC machining. Even minor deviations might result in product failure, harming client satisfaction and the company’s reputation. IoT technology brings in a new era of manufacturing, changing quality control.
The potent real-time monitoring feature is critical. It ensures that errors are rapidly identified and resolved, considerably reducing the potential for waste and the need for labor-intensive rework.
Streamlined Operations
Approximately 70% of companies today use automation for business processes to improve and streamline ordinary, repetitive operations. This pattern extends to CNC machine manufacturers as well. For these businesses, simplifying operations is a key benefit of implementing IoT technology.
Connecting CNC machines to the Internet enables shops to reduce downtime, estimate maintenance requirements, and monitor machine performance in real-time. The machines’ sensors collect data on several features, including vibration, temperature, and production output.
With this data, equipment may be maintained predictably, eliminating unplanned downtime and maintaining constant production levels by servicing units before they fail.
Optimized Use of Energy
Another area where IoT may make a huge difference is energy efficiency. CNC machine companies can detect and eliminate operational inefficiencies by monitoring energy usage in real-time.
IoT systems can cut energy usage during low-demand periods while maintaining production capacity by automatically altering equipment power utilization based on workload.
Improved Compliance and Safety
IoT solutions, for example, can alert operators when a machine exceeds its acceptable limits or when hazardous circumstances arise. Furthermore, by automatically recording production operations and safety precautions, the IoT can help ensure compliance with industrial regulations.
Read: Industry 5.0 vs Industry 4.0: What are the differences? |
Conclusion
In summary, Industry 4.0’s impact on CNC machine operations extends beyond advances in technology to foster a smarter, more agile, and future-ready manufacturing system. Manufacturers get a competitive advantage by embracing Industry 4.0 concepts, which enable them to optimize resource utilization, decrease waste, and boost overall production.
These innovations not only boost immediate operational performance but also position organizations to prosper in a quickly changing industrial environment, making them more resilient to future market difficulties and adjustments.