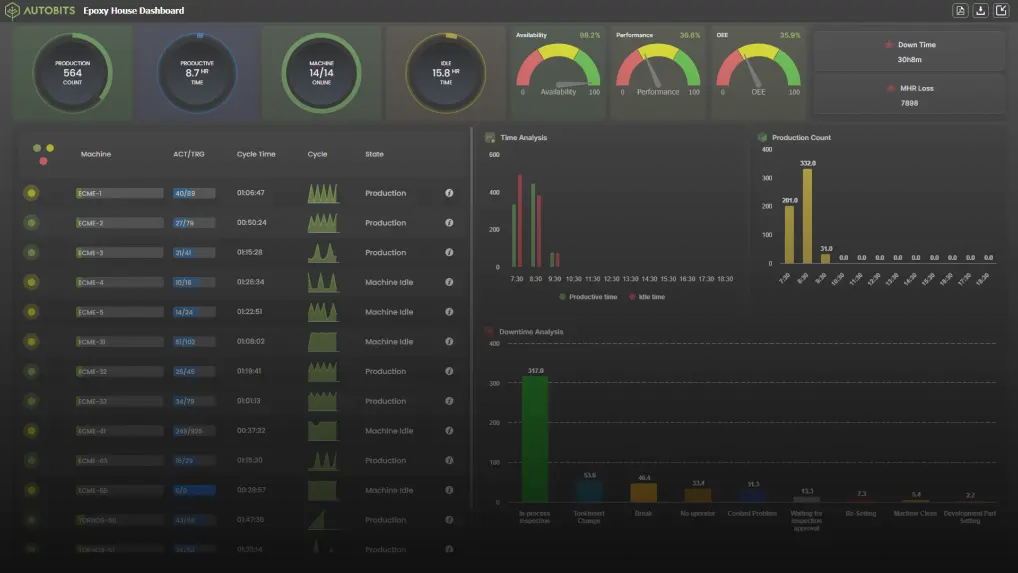
There are multiple terms related to Industry 4.0. Professionals associated directly/indirectly with Industry 4.0 are supposed to know about these terms and jargons. This blog is especially for the users who are puzzled by the terms and jargons thrown at them while attempting to figure out what Industry 4.0 is, and how can it assist, and how much does it cost.
As with any equipment, portions of Industry 4.0 are the domain of the developers of the equipment, while others are the domain of equipment users (this is you). For example, with a CNC machine, you need to know about accuracies, vibration levels, speeds, and so on — in other words, what the machine can accomplish, not how it accomplishes it.
Here is a collection of helpful jargons that you should know, unnecessary stuff that you should avoid, and misinformation that you should avoid.
1. What you’re going to know
Cloud:
The term “cloud” refers to Internet-accessible servers as well as the software and databases that operate on those servers. Cloud servers are located in many data centers across the world.
IOT (Internet of Things) and IIOT (Industrial Internet of Things):
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of physical gadgets that are linked to the internet and collecting and exchanging data all over the world. IOT and IIOT are the same thing, however IIOT refers to how IOT is used in industry.
IT infrastructure:
IT equipment required for implementing the Industry 4.0 system on your shopfloor: IT maintenance staff, recurring IT maintenance cost, LAN (wired/Wi-Fi) in the shop floor, Server (with A/C, physical security, backups, UPS), etc.
Digitalization:
The use of digital technology to modify a company model and generate new revenue and value-producing opportunities is known as digitalization. It is the transition to a digital business.
2. These are things that only software developers worry about, but not you
Cyber-physical system:
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are systems that integrate computer, networking, and physical processes.
Big data:
The large volume of data – both structured and unstructured – that inundates an organization on a daily basis is referred to as big data.
Analytics:
The scientific process of discovering and communicating important patterns in data is known as analytics.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad field of computer science that aims to build smart machines that can perform activities that would typically require human intelligence.
Machine learning (ML):
The science of teaching computers to learn and accomplish things by themselves without being explicitly programmed to do so.
3. Unless they are a part of your operation, you don’t need to know this
For some inexplicable reason, these technologies are (misguidedly) seen as integral to Industry 4.0, and are frequently discussed alongside Industry 4.0 by Experts in speeches and writings. Additive manufacturing, virtual reality, and robotics are a few of their favorites. They make it sound like Industry 4.0 is only possible if you include them in your manufacturing processes.
Additive manufacture:
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is an appropriate name for the technologies that create 3D items by adding layer upon layer of material, whether it’s plastic, metal, or concrete. Additive manufacturing is NOT required for Industry 4.0, and 3D printing machines are not required for Industry 4.0 deployment in your firm.
Robotics:
Industry 4.0 does not necessitate the use of robots. Incorporating Industry 4.0 into your business does not need the use of robots.
High degrees of automation:
It’s possible to have a large number of manually operated machines. All of your material handling might be manual, and manual intervention might be required in every aspect of your business. Industry 4.0 does not necessitate high automation. This is not required for Industry 4.0 deployment in your company.
Virtual truth (VR):
Virtual Reality is a three-dimensional, computer-generating environment with which a human can explore and interact.
Augmented reality (AR):
Augmented reality overlaps the physical world with digital information. For example, you point your mobile phone camera to a machine part, the software will detect the item and provide precise information about the component to be used or serviced.
Action point:
Industry 4.0 is just a term that refers to the automation of data capture, transfer and analysis using machine-connected sensors, the Internet and the cloud. Please use the rules above and make your discussions with professionals associated to Industry 4.0 meaningful, crisp, and swift.