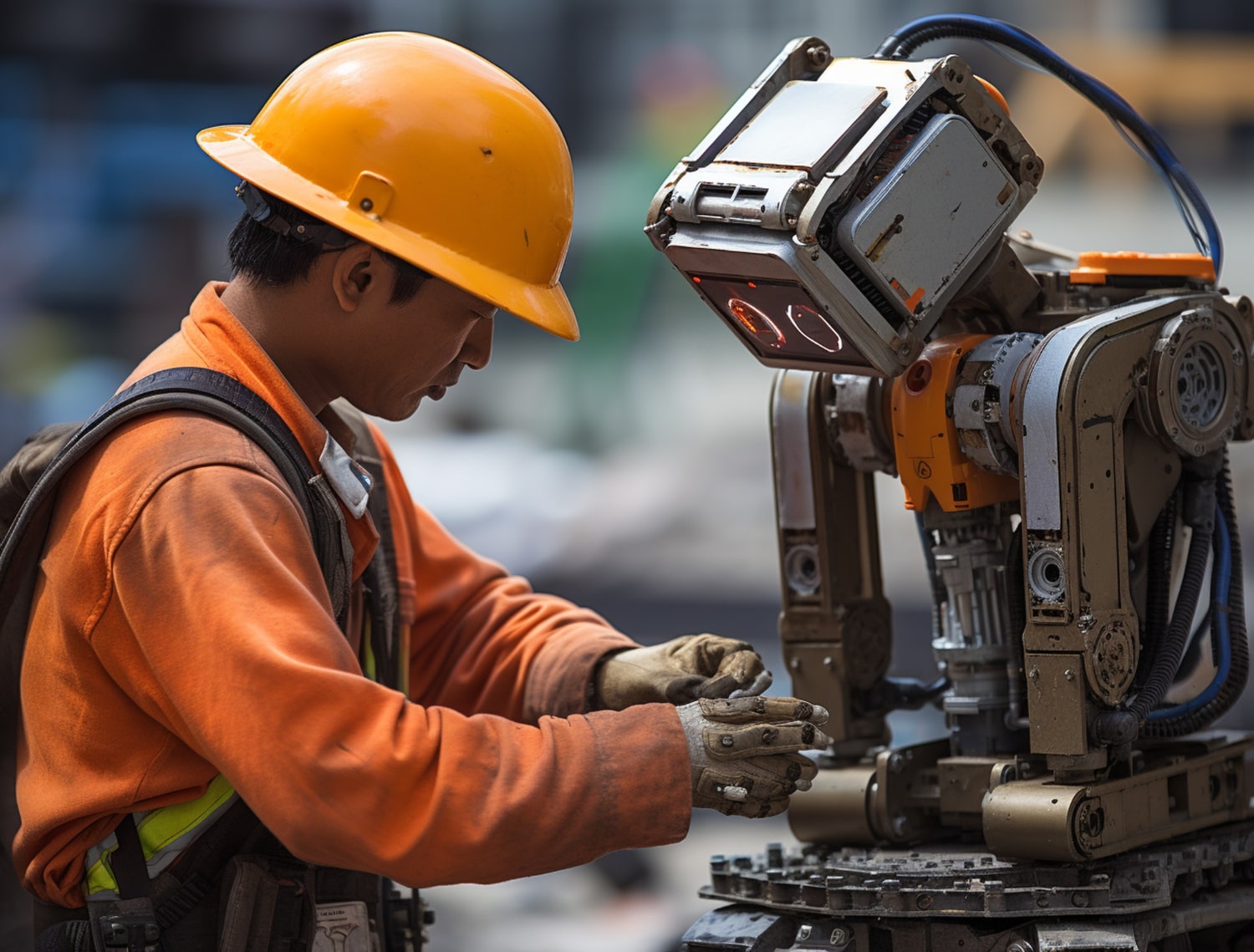
Throughout history, the world has experienced a number of industrial revolutions, all characterized by substantial technological progress. Now we find ourselves in Industry 5.0, marked by a shift to technology working in concert with humans rather than taking their place. While Industry 4.0 embraced automation and improved efficiency, Industry 5.0 focuses on working collaboratively with machines, customization and sustainability.
This guide will address the key ideas, technologies and implications of Industry 5.0 across industries, priming businesses for the future.
The Evolution of Industrial Revolutions
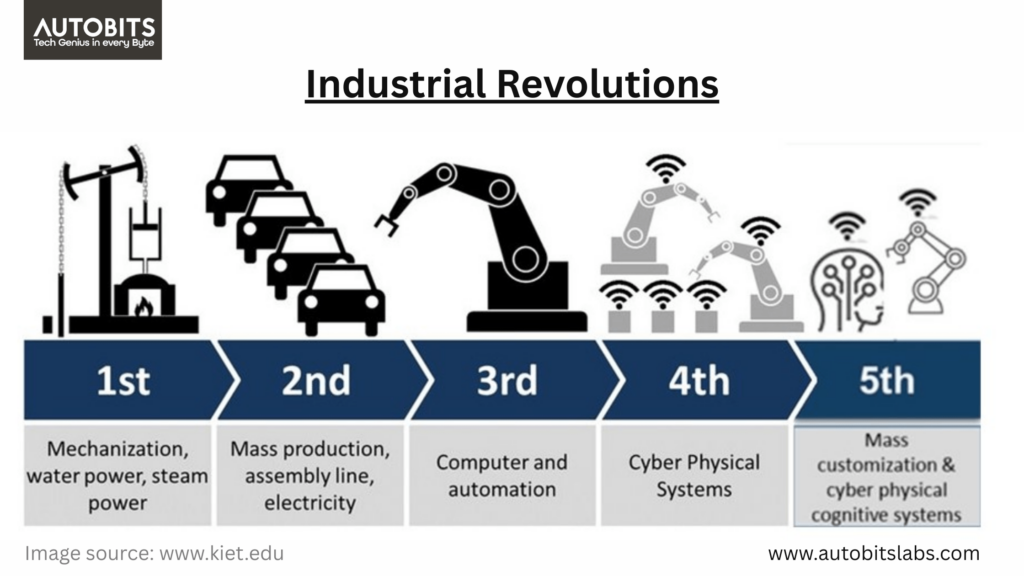
To appreciate the concept of Industry 5.0, it is necessary to look back at industrial revolutions:
Industry 1.0 (Mechanization) – Late 18th Century:
The first industrial revolution happened as steam engines were invented, leading to the mechanization of processes. This industrial shift transformed labor from manual production to machine-based production in factories, resulting in major efficiency improvement.
Industry 2.0 (Mass Production) – Late 19th Century:
The introduction of electricity and assembly lines changed mass production. The moving assembly line developed by Henry Ford was one of the most significant innovations that enabled faster and cheaper production.
Industry 3.0 (Digital Revolution) – Late 20th Century:
The ability to use computers in automated environments and early robotics allowed for rapid improvements in the efficiency and precision of production processes. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) increasingly enabled machines to operate with little or no operator intervention.
Industry 4.0 (Smart Factories) – Early 21st Century:
Factories that were “smart” to various extents began to appear in the early 21st century, controlled by a combination of the IoT, machine-learning, big data, and automation, leading to self-optimizing factories. At this point, machines began to communicate with each other and to make decisions based on sensory data, usually leading to increased output.
Industry 5.0 (Human-Centric) – Present & Future:
Industry 5.0 refers to the current/future trend of returning human intelligence to the equation. Industry 5.0 places emphasis on the collaboration of humans and machines, the sustainability of manufacturing processes, and customized or personalized manufacturing. The goal of Industry 5.0 is the continued use of technology, while ensuring it enhances rather than replaces humans.
Key Principles of Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 presents new ways to combine technological capabilities with human intelligence:
- Human-Machine Collaboration: Workers are supported by smart robots rather than being replaced.
- Personalization & Mass Customization: Organizations are able to produce individualized products at scale.
- Sustainability & Green Manufacturing: Reduced energy consumption enables waste reduction in the production process.
- Ethical AI & Responsible Automation: Fairness, transparency, and security are guaranteed.
- Flexible & Resilient Production: Organizations can respond rapidly to fluctuations in demand.
The Role of Humans in Industry 5.0
One of the biggest changes in Industry 5.0 is an increased emphasis on human intelligence and creativity:
- Workers oversee and optimize automation to ensure quality.
- Creative skills are increasing in value as humans work in innovation.
- Jobs develop in human-AI collaboration, requiring additional skills.
- In the context of workforce adaptation, reskill and upskill programs are essential.
Core Technologies Driving Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 utilizes advanced technologies that bolster human strengths:
- AI with Human Oversight: AI decision-making supports humans rather than replaces them. For example, it can leverage predictive maintenance, data analysis, and process optimizations, while humans provide oversight and rigorous thought.
- Collaborative Robotics (“Cobots”): In distinction to traditional industrial robots, cobots are produced to work alongside human laborers safely, while enhancing productivity in production, logistics, and healthcare. Cobots perform repetitive tasks for humans, allowing the human worker to handle higher-level decision making.
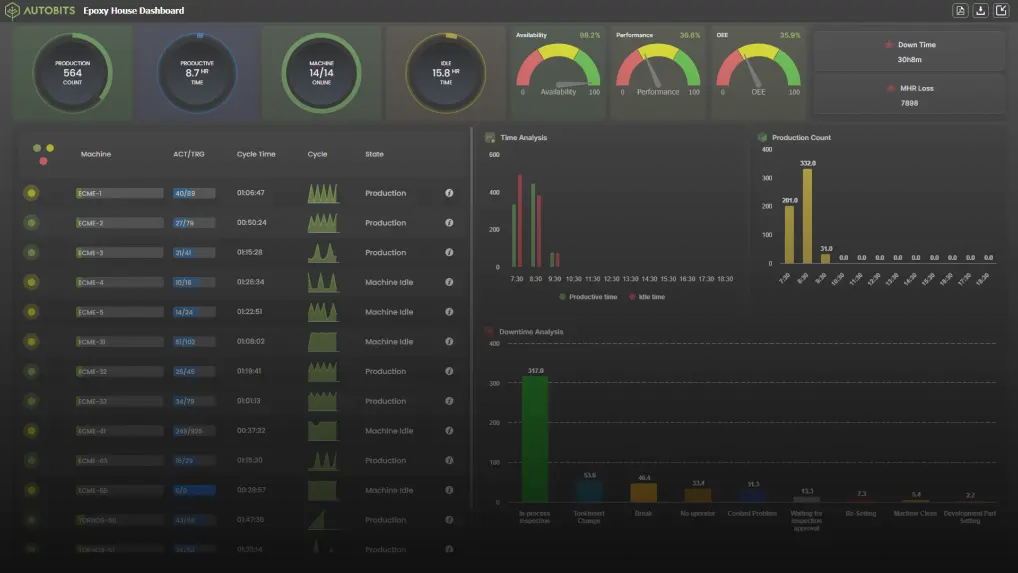
- IoT (human-centric factories): With the Internet of Things, factories can gather real-time data from the Internet of Things, on machines, products, and supply chains. By taking a data-driven approach to business, shifting from paper or oral traditions allows for more significant efficiencies, while reducing downtime and allows for better utilization of human operators for decision making.
- Augmented Reality (“AR”) and Virtual Reality (“VR”): AR and VR improve training of workers, allow visualization of designs, and enhance precision of applications in production. AR and VR allow engineers to evaluate scenarios like the real world, while reducing error rates and improving productivity
- Blockchain for Secure Supply Chains: Blockchain builds authenticity, transparency, security, and traceability to the supply chain and product. It helps companies utilize secure protocols to track and validate the safety and authenticity of materials, reduce fraud, and trust between consumers and manufacturers.
Human-Robot Collaboration
Industry 5.0 differs from conventional automation in that it advocates for collaboration between humans and robots:
- Cobots can increase productivity without taking the jobs of human workers.
- Robots can perform repetitive tasks freeing up workers to engage in more complex work.
- Companies that use cobots report increased efficiency and safety for workers.
- Workers are prepared to manage and work alongside robots via training programs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
One of the most important elements of Industry 5.0 is sustainability:
- Green manufacturing emphasizes the use of renewable energy and sustainable materials.
- A circular economy focuses on reduced waste through re-use of materials.
- Smart factories utilize energy efficiency and CO2 reduction.
- Companies ensure ethical sourcing for a more responsible production.
The Future of Smart Factories
In Industry 5.0, factories move from fully automated systems to human-integrated systems.
- Personalized manufacturing modulates to fit the preferences of consumers.
- Digital twins are creating a virtual model of the factory for subsequent optimization.
- AI leverages data to enhance decision-making with people retaining oversight of production action.
- Factories balance automation with human labor to increase overall efficiency.
The Impact of Industry 5.0 on Different Sectors
Industry 5.0 is already making an impact across many sectors:
- Manufacturing: Smart factories are enabling human-machine collaboration to produce more customized and flexible output.
- Healthcare: Assisted diagnostics through AI, robotic surgeries, and more personalized care are all contributing to better health outcomes for patients.
- Retail & eCommerce: Optimized shopping experiences with powered recommendations and customized products are made possible with the use of AI.
- Education: Interactive tools using AR/VR have enabled the delivery of immersive experiences in education.
- Agriculture: Smart farming optimizes resource use, reduces waste, and generates more crop yield using AI and IoT.
The Role of AI and Automation in a Human-Centric Approach
In Industry 5.0 AI acts as an asset to human workers.
- AI does lead to improvements in efficiency but still requires human oversight and human workers to carry out the tasks the AI does not have the capabilities to do.
- Ethical AI can play a large role in decision making to help eliminate bias and create fairness.
- AI systems assist humans or will automate systems that help make use of human creativity instead of replacing job roles.
- AI does assist us in decisions and doing things but will not dictate to us; humans will continue to innovate.
Workforce Transformation in Industry 5.0
When advances in technology preview new jobs, workers will have to adapt:
- Reskilling and upskilling opportunities will ensure that employees can be prepared for an AI-induced job market.
- New job roles will emerge during the transition to AI that focus more on human-machine interaction.
- Remote work will grow with technology enabling digital environments.
- Schools will embed knowledge of AI and technology in the curriculum to better prepare future generations for opportunities today and into the future.
Challenges in Adopting Industry 5.0
Despite its benefits, Industry 5.0 faces some challenges:
- Workforce resistance to change requires cultural shifts.
- High costs of implementation slow adoption.
- Cybersecurity risks increase as digital technologies expand.
- Data privacy concerns arise with AI-driven automation.
Government Policies and Regulations
Governments play a role in shaping Industry 5.0 adoption:
- Regulations ensure ethical AI and responsible automation.
- Policies support sustainability through incentives for green manufacturing.
- Educational reforms prepare workers for AI-driven industries.
- Global initiatives promote human-centric industrial growth.
Preparing Your Business for Industry 5.0
Businesses must take steps to adapt to Industry 5.0:
- Assess Current Technology Adoption: Evaluate your existing digital infrastructure and identify areas for improvement.
- Invest in AI, Robotics, and Upskilling Programs: Train employees to work with advanced technologies while integrating smart automation tools.
- Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Manufacturing: Adopt eco-friendly practices, minimize waste, and enhance transparency.
- Develop Strategies for Human-Technology Collaboration: Foster a company culture that embraces innovation, encourages AI adoption, and ensures employees feel empowered rather than threatened by automation.
The Future of Industry 5.0
Looking ahead, Industry 5.0 will continue to evolve:
- AI and quantum computing will enhance efficiency.
- New business models will emerge around personalized production.
- Technology will continue to integrate with human expertise.
- The balance between automation and human creativity will define the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Industry 5.0?
Industry 5.0 represents the next phase of industrial evolution, centered around human-machine collaboration, sustainability, and customized or personalized production.
How does Industry 5.0 compare to Industry 4.0?
While Industry 4.0 focuses on automation and artificial intelligence, Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-AI collaboration and sustainability.
Which industries will see the biggest benefits from Industry 5.0?
Industries that will see the biggest impact are manufacturing, healthcare, retail, education, and agriculture.
How should businesses position themselves for Industry 5.0?
Businesses must invest in artificial intelligence, robotics, workforce training, and sustainable practices.
Is Industry 5.0 happening now?
Many companies implementing Industry 4.0 strategies are already striking their own human intelligence strategically alongside AI-enabled processes.