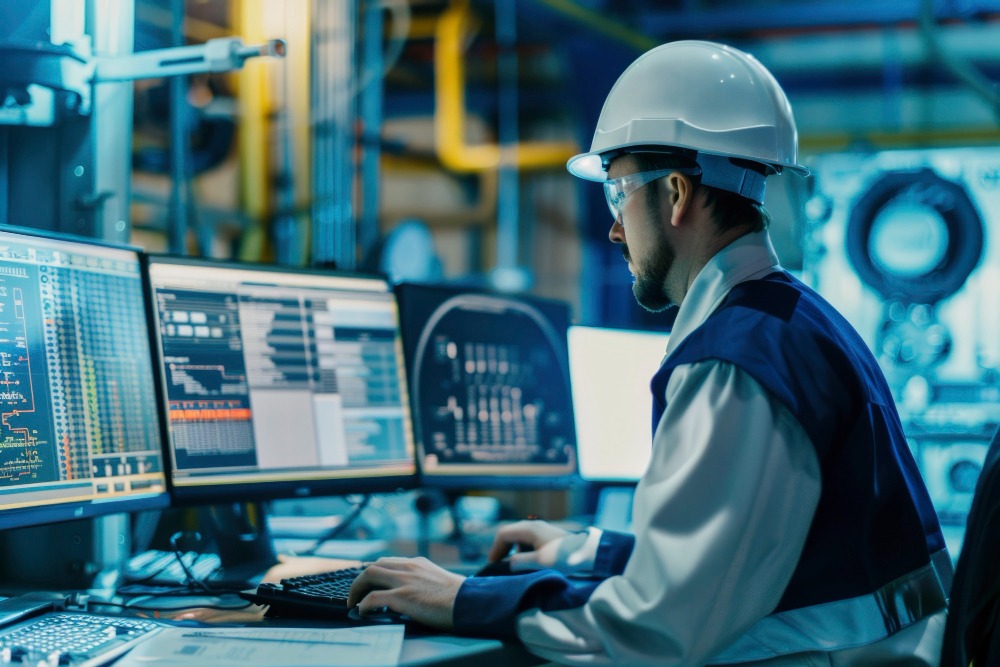
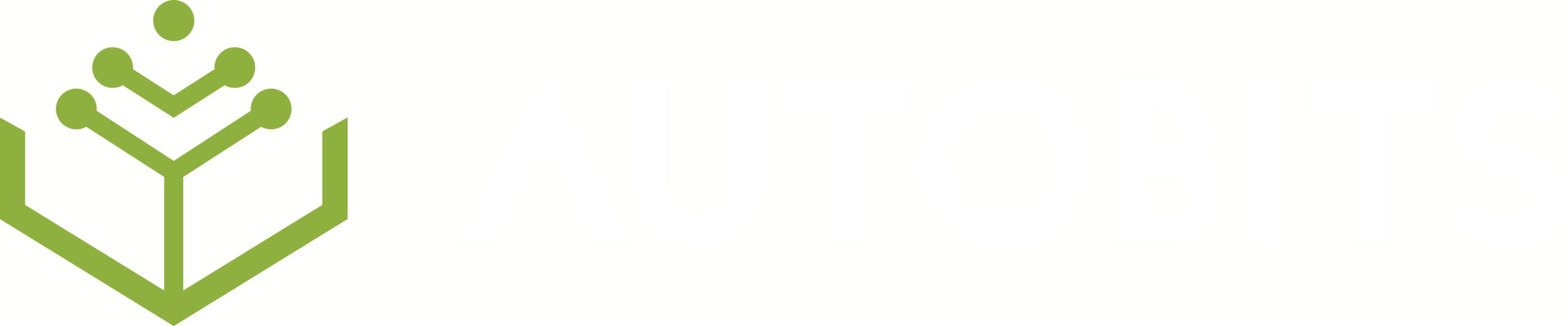In the competitive landscape that is manufacturing, equipment uptime, productivity, and efficiency can no longer be optional, but are essential. Machine Condition Monitoring is an important aspect of machine health and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). Enterprise-level machine condition monitoring aims to get manufacturing operations away from reactive maintenance activities and approach a proactive, condition-based maintenance strategy.
In this blog post, we will cover everything you need to know about machine condition monitoring, from how it differs from general machine monitoring, benefits, key condition monitoring techniques, and how Autobits’ CNC Machine Monitoring Software can help modern factories achieve smarter factory operations.
What is Machine Condition Monitoring?
Machine Condition Monitoring, collecting and analyzing data about machine health, track key parameters like temperature, vibration, pressure, and noise to detect early signs of wear, imbalance, misalignment, or faults.
The proactive nature of condition monitoring allows teams to assess machine conditions, identify issues, and schedule maintenance before breakdowns without waiting for machine failures to occur, which often means costly downtime. Condition monitoring increases productivity.
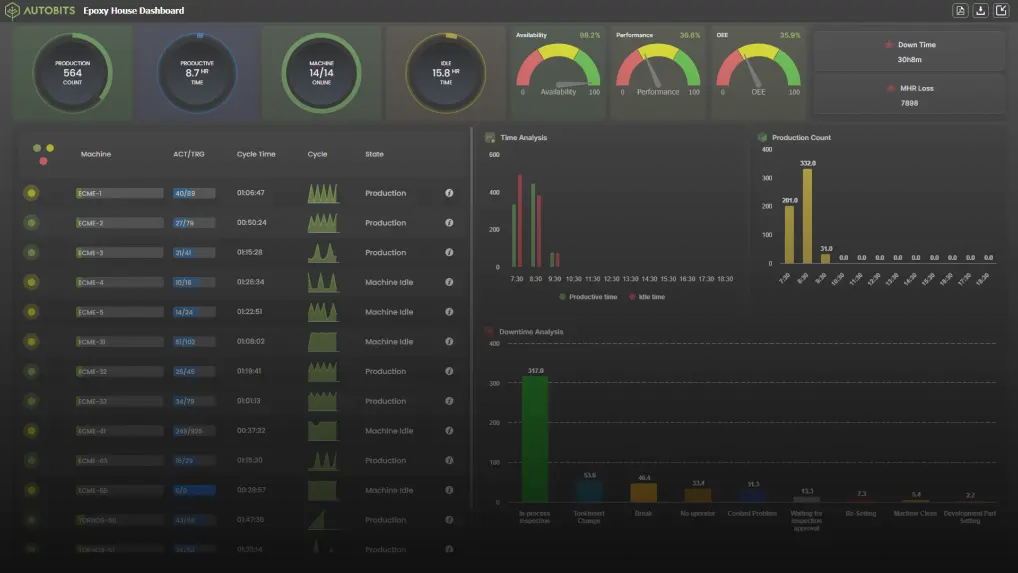
Difference Between Condition Monitoring and Machine Monitoring
Though often used interchangeably, there’s a difference between Machine Monitoring and Condition Monitoring:
Key Differences Explained
- Machine Monitoring focuses on whether your machine is running or not, and presents very basic information such as uptime and downtime. Machine monitoring allows a team to be reactive to a stoppage, but it does not give any insight into what is causing the actual stoppage or malfunctions, or how to prevent them in the future.
- Condition monitoring takes a step further by continually monitoring data points related to parameters (such as vibration, thermal input or output, pressure, etc.) to understand how each component performs and assess its health. This additional scope allows a team to analyze if an asset is failing or close to the catastrophic failure point when it is still in the operating stage. This empowers an organization to perform scheduled maintenance only when it is genuinely needed, reducing costs associated with unnecessary maintenance and helping reduce the risk of catastrophic asset failure.
- In short, machine monitoring provides a standard report for a team to understand their currently operational assets but does not offer the type of deeper analytics required for advancement in proactive, data-driven maintenance. The condition monitoring extension to machine monitoring is the next step, and condition monitoring will offer the insights and diagnostics required to optimize each asset’s lifespan and operational performance.
Finally, condition monitoring is a more mature and analytics-driven extension of basic machine monitoring, allowing organizations to move away from purely reactive maintenance regimes and toward potentially predictive maintenance strategies by relying on asset performance analysis and monitoring.
Why is Condition Monitoring Important?
Without condition monitoring, businesses rely on scheduled maintenance or reactive repairs—both of which have their drawbacks:
- Scheduled maintenance may result in unnecessary downtime.
- Reactive maintenance leads to unplanned shutdowns and higher repair costs.
With condition monitoring, manufacturers can:
- Detect faults early
- Avoid catastrophic failures
- Extend machine life
- Shift to a condition-based maintenance (CBM) model.
- Improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
Benefits of Condition Monitoring
Here are the key benefits of implementing a machine condition monitoring system:
- Early Detection of Problems: Continuous monitoring allows for early identification of problems or degradation in equipment, enabling timely action prior to minor issues or faults escalating to a major failure.
- Less Downtime and More Uptime: When problems can be detected in advance there is less likelihood for a sudden equipment failure, making the equipment available and allowing production to resume more promptly
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Maintenance occurs based on what is actually occurring to the equipment instead of preordained schedules of maintenance. As a result, there will be much less unneeded maintenance and lower associated costs.
- Asset Longevity: Timely maintenance and repairs reduce excessive wear and extend the life cycle of the equipment while reducing the need for premature disposal.
- Better Maintenance Planning: Having real-time and historical records of the equipment allows for better prioritizing and planning of maintenance activities, as you can see where resources are being assigned.
- Improved Efficiency during Operations: If the equipment is operating and maintained as designed, organizations will have an opportunity to increase production, reduce waste, and improve operational performance.
- Improved Safety: Monitoring safety-implicating parameters can monitor the potential rapid identification of hazardous circumstances, making the workplace safer and reducing the risk of injury.
- Better Use of Resources: Condition monitoring assists in the efficient use of energy, material, and labour by recognizing if operating assets are outside of optimal parameters, resulting in cost savings and sustainability.
- Improved Decision Making: Access to complete, real-time information allows maintenance teams to make sound decisions about equipment performance, repairs, and investments.
- Competitive advantage: Organizations that set, implement, and utilize sound condition monitoring can deliver higher quality products and services with less interruption to their activities and thus improve reliability, customer satisfaction, and market position.
What Conditions Can You Monitor On A Machine?
Condition monitoring systems track various machine health parameters, such as:
- Vibration: Detects imbalance, misalignment, and bearing deterioration
- Temperature: Identifies overheating in motors or stators.
- Pressure: Measures the health of fluid systems
- Noise/Acoustics: Traces anomalies in bearings or gearboxes
- Lubrication (levels): Detects lubricants for rotating equipment
- Electric Current/Voltage: Detects electrical faults or inconsistencies in load
Machine Condition Monitoring Techniques
Several techniques are used depending on machine type and criticality:
- Vibration Analysis: Tracks mechanical failures such as misalignment, unbalance, and looseness
- Thermography (Infrared Monitoring): Locates hot spots in electrical or mechanical systems
- Ultrasonic Testing: Locates air leaks, steam traps and bearing conditions
- Oil Analysis: Analyzes lubricant condition, wear particles in oil
- Motor Current Signature Analysis (MCSA): Utilized to identify rotor bar problems and load issues in motors
- Acoustic Emission Monitoring: Detects high-frequency sound signals from deformations of materials or cracks.
Enabling Condition-Based Maintenance
One of the most valuable benefits of machine condition monitoring technology is that it allows for Condition Based Maintenance (CBM). Rather than following a schedule based on calendar weeks or trigger conditions, maintenance can now occur when the sensors detect a potential problem.
This results in:
- Lower maintenance overheads
- Reduced machine failures
- Optimized resource allocation
Alarms, Notifications, and Automation
An intelligent monitoring system doesn’t just collect data—it reacts in real time. Alerts and notifications can be set for critical thresholds. When abnormalities are detected, the system can automatically:
- Notify the maintenance team.
- Trigger alarms on dashboards
- Generate service tickets
- Stop the machine in critical scenarios.
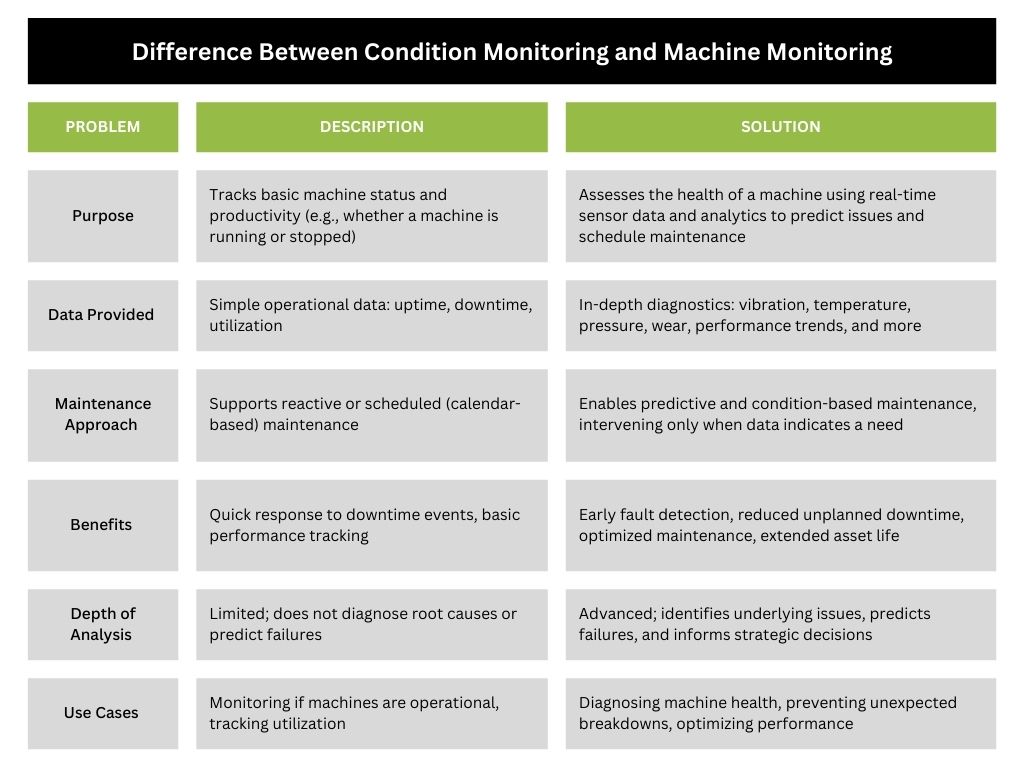
Increase Your Plant’s Efficiency with Autobits CNC Machine Monitoring Software
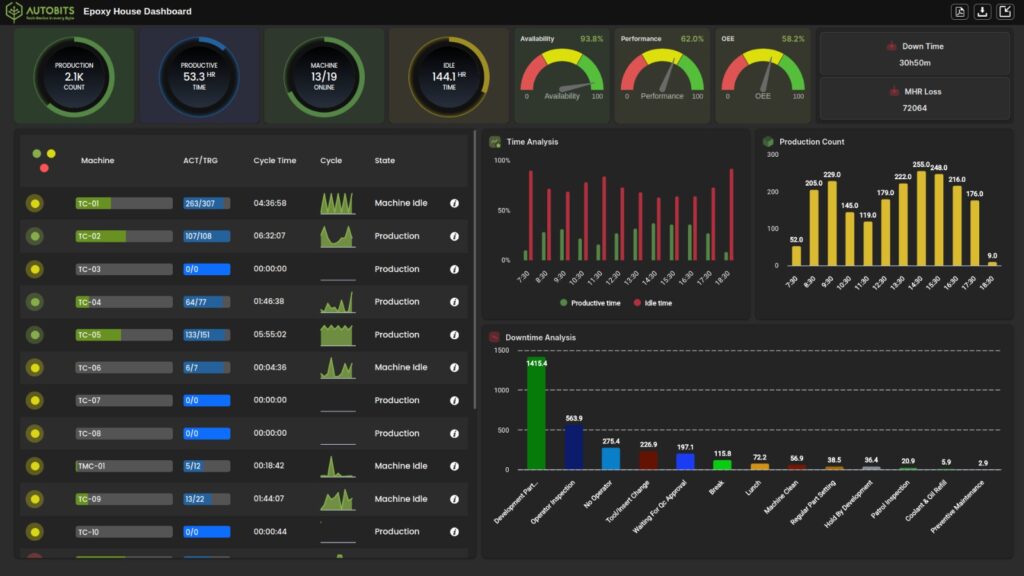
To maximize the advantages of machine condition monitoring, you need a reliable platform with real-time information, data visualization and smart alerting.
Autobit’s Machine Monitoring Software allows manufacturers to monitor the operational and health parameters of their CNC Machines. With capabilities such as:
- Real-time dashboards
- Condition-based alerts
- Sensor integration (vibration, heat, etc.)
- OEE tracking and reporting
…you’ll be able to make more intelligent maintenance decisions and improve the overall efficiency of your plant.
Autobits allows you to take the next step towards Industry 4.0 and combines machine monitoring and condition monitoring in one easy-to-use and powerful platform.
Conclusion
Machine condition monitoring is no longer a luxury item but is necessary for today’s manufacturers hoping to remain competitive. Machine condition monitoring provides early issue detection and data-based decisions for maintenance, thus offering businesses the potential to protect their assets, lower their costs, and achieve higher OEE.
Autobits’ CNC Machine Monitoring Software offers businesses the opportunity to increase efficiency across the plant by implementing a machine health strategy and taking the first steps toward excellence in predictive maintenance.
FAQs
What distinguishes preventive maintenance from condition-based maintenance?
Preventive maintenance is performed at fixed intervals regardless of the condition of the equipment, while condition-based maintenance utilizes real-time information to maintain equipment only when required.
What standard parameters are monitored during machine condition monitoring?
Standard parameters include vibration, temperature, pressure, noise, and lubrication levels.
How does condition monitoring improve OEE?
Condition monitoring improves OEE through reduced downtime and minimizing performance losses due to equipment failure, thus improving Availability and Performance.
Is condition monitoring possible for older machines?
Condition monitoring can also be performed using retrofit sensors and external monitoring devices with older, legacy equipment.
What industries are benefited from machine condition monitoring?
Condition monitoring practices can substantially benefit manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, oil & gas, and energy-related industries.