The eights pillars or activities of Total Production Maintenance (TPM) focus on preventive and proactive measures to improve machine reliability. They are:
 Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous Maintenance- Planned Maintenance
- Quality Maintenance
- Focused Improvement
- Early Equipment Management
- Training and Education
- Safety, Health, Environment
- TPM in Administration
- Autonomous Maintenance
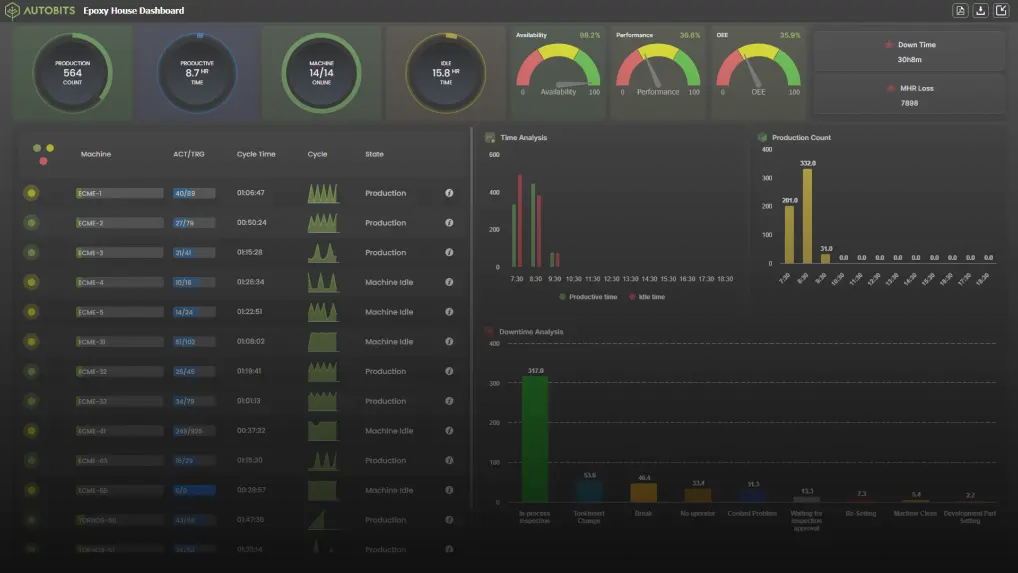
Operators are handed over the responsibility for routine maintenance such as inspection, lubricating, cleaning. This gives an opportunity to the operator to increase his knowledge of the equipment. The feeling of ownership prevails in operators as they clean and lubricate the equipment. At higher level, it helps to identify emerging issues before they fail altogether. Iot and Machine Automation are highly interlinked.
- Planned Maintenance
Maintenance schedules are planned based on preventive and proactive failure rates which reduces unplanned downtime. On the other hand, it permits to plan the maintenance period during the time when equipment is not scheduled for running and production.
- Quality Maintenance
Error detection and prevention is designed in the production phase. It focuses on eliminating root source of defects and thus improving project quality. Root Cause Analysis methodology is applied to remove such defects. By reducing amount of defects, it helps to reduce sudden expenses.
- Focused Improvement
Incremental improvements in equipment operations when a limited number of employees work together. Identification of recurring issues becomes easier which can be resolved by functional teams. This group of limited number of people is usually a collection of various talents who build an engine for constant up-gradation. This outcasts open innovation in the industries.
- Early Equipment Management
Directions to improve the design of new equipment are derived through practical knowledge and understanding of manufacturing which is obtained from TPM. This way objectives of the performance level for new equipment can be obtained much faster. Maintenance too, becomes simpler because of the involvement of employees before installation.
- Safety, Health, Environment
It is important to maintain a healthy and safe workplace. It eliminates safety and potential health risks as it precisely targets the goal of hazard-free and accident-free working environment.
- TPM in Administration
It focuses at applying the TPM abilities in the administrative functions. Beyond plant floor, the extended TPM benefits can be attained by addressing the waste in the administrative functions. Operations such as scheduling, order processing and procurement can be improvised.