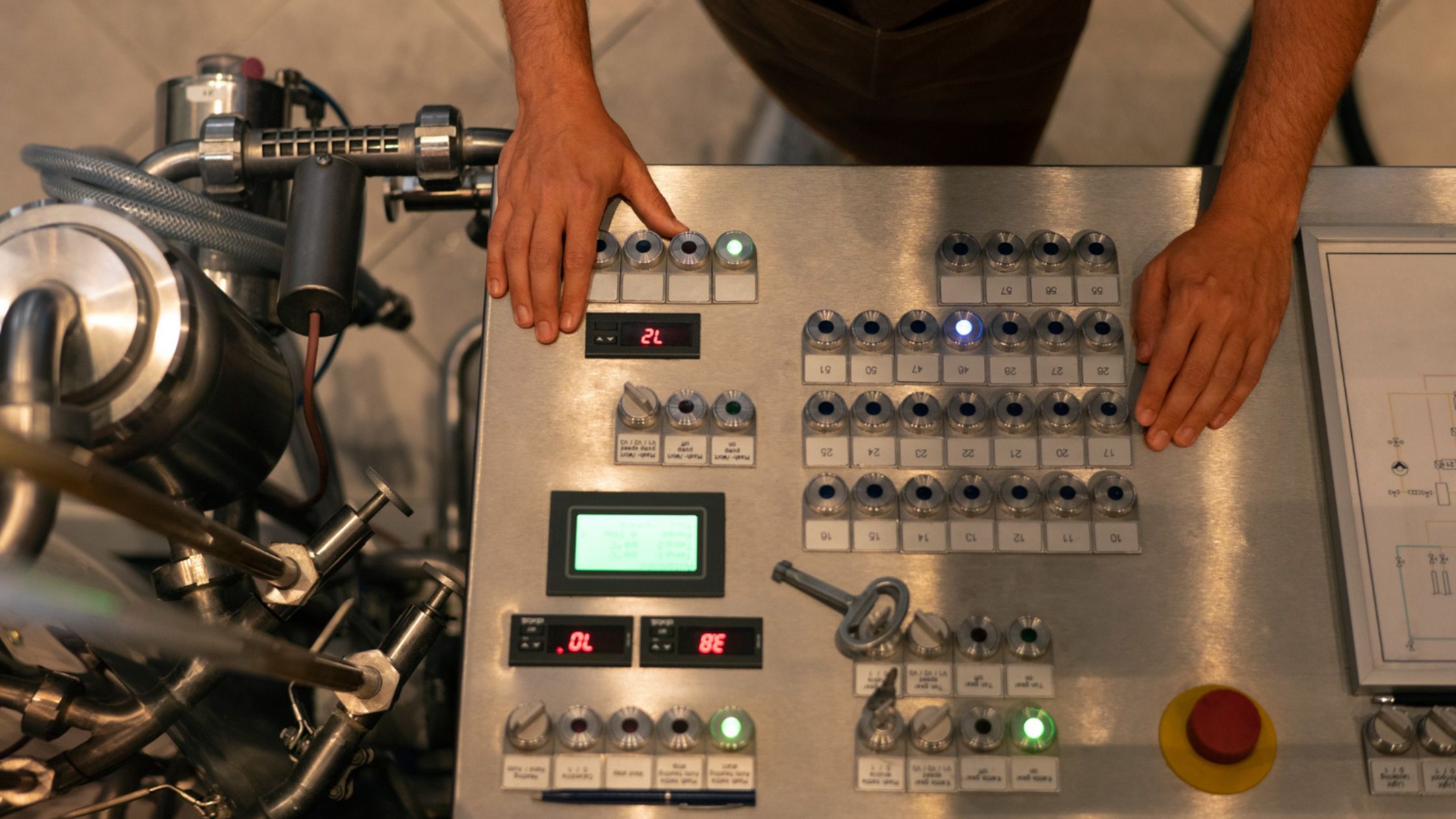
The CNC controller is the heart of every CNC machine. It turns digital code into precise movements that shape materials with unmatched accuracy. Even the best machines cannot perform at their full potential without a reliable CNC controller.
With manufacturing moving toward automation, Industry 4.0, and smart factories, choosing the right CNC controller brand is more important than ever. This blog explores what CNC controllers are, how they work, the top global brands shaping the market, and what trends to watch in the future.

What is a CNC Controller?
A CNC controller is a CNC system’s central processing unit (CPU). It interprets digital program instructions (G-code and M-code) and converts them into electrical signals that drive motors, actuators, and auxiliary functions.
Definition:
The CNC controller, often called the Machine Control Unit (MCU), automates machine operations such as cutting, drilling, milling, turning, and even additive manufacturing.
Core Functions:
- Program Execution: Runs NC programs to perform machining steps.
- Motion Control: Directs precise movements of machine axes.
- Automation Integration: Coordinates with sensors, I/O devices, and feedback loops.
- Versatility: Works across different machining processes, including subtractive, additive, and hybrid systems.
How Does a CNC Controller Work?
A CNC controller automates tool and workpiece movement based on digital instructions, ensuring repeatability and high accuracy.
Working Principle
- Program Input: G-code generated from CAD/CAM is fed into the controller.
- Decoding & Processing: The MCU interprets the commands.
- Execution: The controller sends signals to motors, actuators, and spindles.
- Feedback Control: Sensors ensure accuracy through closed-loop systems.
- Real-Time Adjustment: Deviations are corrected instantly.
Key Components
- Machine Control Unit (MCU): The brain of the system.
- Servo Drives & Motors: Control precise movements.
- Feedback System: Encoders/scales for closed-loop accuracy.
- Input/Output Devices: These are for program loading and system monitoring.
Execution Cycle:
The controller continuously processes G-code, moves machine components, and adjusts based on feedback to maintain design precision.
Example: In a CNC lathe machine, the controller ensures that the cutting tool follows programmed paths while automating coolant, spindle, and tool changes.
CNC Controller Market Statistics
The global CNC controller market size was valued at USD 3.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 4.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% (Source: MarketsandMarkets).
Asia-Pacific dominates the market, led by Japan, China, and South Korea.
FANUC (Japan) and Siemens (Germany) hold a combined ~45% global market share in CNC controllers (Source: Mordor Intelligence).
Growth is driven by:
- Demand for automation in aerospace & automotive
- Rising adoption of 5-axis and multi-axis machining
- Industry 4.0 & IoT integration in CNC systems
Top CNC Controller Brands in the World (Detailed)
Only a few brands dominate the global stage when it comes to CNC controllers due to their technological innovation, reliability, and market penetration. Below are the top 10 CNC controller brands in the world.
1. FANUC (Japan)
- Overview: FANUC (Fuji Automatic Numerical Control) is the global leader in CNC controllers, robotics, and factory automation. Founded in 1956, FANUC has shaped CNC technology for decades.
- Key Products: FANUC Series 30i/31i/32i Model B, Power Motion i-Model A.
- Strengths:
- Extremely reliable and robust controllers.
- Industry leader in 5-axis and high-speed machining.
- Strong integration with robotics and automation.
- Industries: Automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery, consumer electronics.
- Market Position: Holds ~20% global CNC controller market share (Source: Statista).
2. Siemens (Germany)
- Overview: Siemens’ SINUMERIK CNC controllers are widely recognized for precision and innovative manufacturing solutions. They are the backbone of Industry 4.0 integration.
- Key Products: SINUMERIK 828D, SINUMERIK 840D sl, SINUMERIK ONE (digital twin-based).
- Strengths:
- Advanced automation and digital twin technology.
- User-friendly interface with conversational programming.
- Strong presence in Europe & smart factories worldwide.
- Industries: Aerospace, defence, precision machining, automotive.
- Market Position: Siemens and FANUC together dominate the high-end CNC controller market globally.
3. Mitsubishi Electric (Japan)
- Overview: Mitsubishi CNC controllers are known for speed and precision, especially in Asian manufacturing hubs. Their M8 series is widely used in high-speed applications.
- Key Products: M800/M80 Series, C80 Series.
- Strengths:
- High-speed, high-accuracy processing.
- Strong integration with Mitsubishi drives and automation systems.
- Cost-effective compared to FANUC/Siemens.
- Industries: Electronics, automotive, and metal cutting.
- Market Position: Leading player in Asia-Pacific CNC markets.
4. Heidenhain (Germany)
- Overview: Heidenhain pioneered precision CNC controls and motion feedback systems. Their controllers excel in toolroom and mould/die applications.
- Key Products: TNC 640, TNC 320, TNC 620.
- Strengths:
- Exceptional 5-axis machining capabilities.
- Integrated touch-screen user interfaces.
- Advanced motion control with encoders.
- Industries: Medical devices, aerospace, mould & die making.
- Market Position: Preferred brand for ultra-precision machining.
5. Mazak (Japan)
- Overview: Mazak is both a machine tool builder and controller innovator. Its proprietary MAZATROL controllers simplify complex machining.
- Key Products: MAZATROL SmoothAi, SmoothX, SmoothG.
- Strengths:
- Conversational programming makes learning easier.
- Strong AI integration with SmoothAi.
- Designed specifically for Mazak machines.
- Industries: Metal cutting, automotive, aerospace.
- Market Position: Popular in metalworking industries worldwide.
6. Haas Automation (USA)
- Overview: Haas offers CNC controllers tailored to its machines, making them very user-friendly and cost-effective. Haas dominates the North American mid-market.
- Key Products: Haas Next Generation Control (NGC).
- Strengths:
- Simplified interface for machinists and students.
- Integrated networking, tool management, and real-time monitoring.
- Affordable compared to high-end European/Japanese brands.
- Industries: Education, job shops, small-to-medium manufacturers.
- Market Position: Best-selling CNC brand in the USA & educational sector.
7. Fagor Automation (Spain)
- Overview: Fagor is a European innovator specializing in flexible CNC controllers for multitasking machines.
- Key Products: Fagor 8065, Fagor 8055i.
- Strengths:
- Great for multitasking and complex automation.
- Strong customisation capabilities.
- Excellent service and support in Europe.
- Industries: Metal cutting, general machining, and research labs.
- Market Position: Strong presence in Europe and Latin America.
8. NUM (France/Switzerland)
- Overview: NUM is an early pioneer of CNC control systems and continues to innovate with the Flexium+ series.
- Key Products: Flexium+, NUMDrive X.
- Strengths:
- Strong in large multi-axis & channel setups.
- Customized CNC solutions for OEMs.
- Focus on complex automation tasks.
- Industries: Aerospace, large equipment manufacturing, and high-precision machining.
- Market Position: Niche but respected in high-end industrial sectors.
9. Okuma (Japan)
- Overview: Okuma develops machine tools and CNC controllers (OSP series), ensuring deep integration and efficiency.
- Key Products: OSP-P300A, OSP-P500.
- Strengths:
- Proprietary Thermo-Friendly Concept for stable machining.
- Easy-to-use and integrated with Okuma machines.
- High reliability and smooth cutting control.
- Industries: Heavy machinery, automotive, aerospace.
- Market Position: Preferred by industries needing machine-controller synergy.
10. HuazhongCNC (China)
- Overview: HuazhongCNC is a fast-growing Chinese CNC controller manufacturer, aiming for global leadership.
- Key Products: HNC-848D, HNC-808D, HNC-818.
- Strengths:
- Strong R&D in intelligent controls and AI integration.
- Affordable solutions compared to Japanese/European brands.
- Considerable domestic market support in China.
- Industries: Automotive, heavy machinery, and general manufacturing.
- Market Position: Leading CNC brand in China, rapidly expanding globally.
CNC Controller Comparison Table: Which Brand Fits Your Needs?
| Brand | Country | Key Products | Strengths | Industries Served | Market Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FANUC | Japan | Series 30i/31i/32i, Power Motion i | Reliability, robotics integration, 5-axis capability | Automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery | Global leader (~20% share) |
| Siemens | Germany | SINUMERIK 828D, 840D, ONE | Digital twin, smart factory integration, precision | Aerospace, automotive, defense | Strong in Europe & Industry 4.0 |
| Mitsubishi | Japan | M800/M80, C80 Series | High-speed machining, accuracy, cost-effective | Electronics, automotive, metal cutting | Strong presence in Asia |
| Heidenhain | Germany | TNC 640, 320, 620 | Precision, advanced 5-axis machining, encoders | Medical, aerospace, mold & die | Niche, ultra-precision |
| Mazak | Japan | MAZATROL SmoothAi, SmoothX, SmoothG | Conversational programming, AI integration | Metal cutting, aerospace, automotive | Proprietary for Mazak machines |
| Haas | USA | Next Generation Control (NGC) | User-friendly, affordable, strong support | Education, job shops, small-mid shops | Dominant in North America |
| Fagor | Spain | 8065, 8055i | Multitasking, customization, flexibility | General machining, research labs | Strong in Europe & Latin America |
| NUM | France/Switzerland | Flexium+, NUMDrive X | Large multi-axis setups, OEM solutions | Aerospace, heavy equipment, high-precision | Niche, high-end automation |
| Okuma | Japan | OSP-P300A, OSP-P500 | Machine-controller synergy, thermal stability | Heavy machinery, automotive, aerospace | Popular for integrated solutions |
| HuazhongCNC | China | HNC-848D, 808D, 818 | AI-driven controls, affordability, rapid R&D | Automotive, general manufacturing | Leading in China, expanding globally |
Which CNC Machine Controller is Best? (Factors to Consider)
There is no “one-size-fits-all” CNC controller. The best choice depends on your industry, machine type, budget, and future automation goals. Below are the key factors to consider when selecting a CNC controller brand:
1. Reliability & Accuracy
- CNC machining demands precision within microns.
- Brands like FANUC, Siemens, and Heidenhain are trusted for repeatability and zero downtime, making them ideal for aerospace and medical applications.
2. Ease of Use & Programming
- Controllers with conversational programming (like Mazak’s MAZATROL or Haas NGC) simplify operations for machinists with limited G-code knowledge.
- User-friendly interfaces reduce training time and errors.
3. Machine Compatibility
- Some controllers are universal (FANUC, Siemens, Mitsubishi), while others are proprietary (Mazak, Okuma).
- If you use mixed-brand machines, go for controllers with broad compatibility.
4. Automation & Smart Factory Integration
- For Industry 4.0 adoption, controllers must support:
- IoT connectivity
- Digital twin simulation
- Real-time monitoring & AI integration
- Siemens and FANUC lead in this space.
5. After-Sales Support & Training
- Even the best hardware is only as good as the service support behind it.
- Haas is popular in the USA for its excellent customer service and training programs.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
- High-end controllers (FANUC, Siemens, Heidenhain) deliver unmatched precision but at a premium.
- HuazhongCNC (China) and Haas (USA) offer affordable yet reliable small and medium shops.
7. Industry-Specific Needs
- Automotive & heavy industries: FANUC, Siemens, Mitsubishi.
- Aerospace & medical: Heidenhain, Siemens.
- Educational/job shops: Haas, Fagor.
- General machining & SMEs: HuazhongCNC, NUM, Fagor.
Bottom line:
- Best for high-end precision: Heidenhain, Siemens.
- Best for cost-effective learning & SMEs: Haas, HuazhongCNC.
- Best for global industry integration: FANUC, Mitsubishi.
- Best proprietary ecosystems: Mazak, Okuma.
Future Trends in CNC Controller Technology
The CNC controller industry is evolving rapidly with AI, IoT, and smart manufacturing reshaping how machines operate. Here are the key trends to watch:
1. AI-Powered CNC Controllers
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables self-optimizing controllers to adjust machining parameters in real time.
- Example: AI-driven tool wear prediction reduces downtime and increases tool life.
- By 2030, AI integration in CNC is expected to reduce unplanned downtime by up to 40% (Source: Deloitte).
2. IoT and Cloud Connectivity
- Controllers are now designed with IoT sensors and edge computing for real-time monitoring.
- Cloud integration allows manufacturers to analyze performance across multiple plants.
- This is essential for predictive maintenance and remote troubleshooting.
3. Digital Twin Technology
- Siemens has already launched SINUMERIK ONE, the first controller with a complete digital twin.
- Digital twins allow virtual simulation of machining before actual production, reducing setup time and material waste.
- Adoption of digital twin technology is expected to grow at ~35% CAGR by 2028 (Source: MarketsandMarkets).
4. Adaptive Machining
- Future controllers will feature adaptive machining algorithms that automatically respond to vibration, cutting force, and temperature changes.
- This results in higher precision, reduced scrap, and longer tool life.
5. Human-Machine Collaboration
- Controllers are moving toward more intuitive, touch-based, and voice-controlled interfaces.
- This will allow operators with minimal CNC experience to handle complex machining.
6. Cybersecurity in CNC Controllers
- Greater connectivity comes with risk. Future controllers will integrate advanced encryption, access control, and anomaly detection to protect against cyberattacks.
7. Sustainability & Energy Efficiency
- Next-gen CNC controllers will optimize energy use in machining, reducing carbon footprints.
- For example, FANUC has already introduced energy-saving servo technology.
CNC Controllers and the Role of Machine Monitoring

Even the most advanced CNC controller whether FANUC, Siemens, or Heidenhain; focuses on accurately executing machining operations. However, once machines are running, manufacturers often face challenges such as:
- Untracked downtime
- Energy waste during idle times
- Unnoticed tool wear or inefficiencies
- Difficulty in analysing machine utilisation
This is where machine monitoring software comes in as the perfect complement to CNC controllers.
Why Monitoring Matters Alongside Controllers
- A CNC controller ensures precision at the machine level, while monitoring software ensures efficiency at the factory level.
- By integrating monitoring systems, manufacturers can:
- Gain real-time visibility of machine performance.
- Track OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) automatically.
- Receive alerts for downtime or anomalies before they escalate.
- Analyse historical data for continuous improvement.
Example in Practice
Imagine a plant running multiple CNC machines with FANUC and Siemens controllers. The controllers execute machining tasks flawlessly, but without monitoring:
- Operators may not notice if a machine is idle for hours.
- Managers may lack data on energy consumption.
- Preventive maintenance becomes reactive.
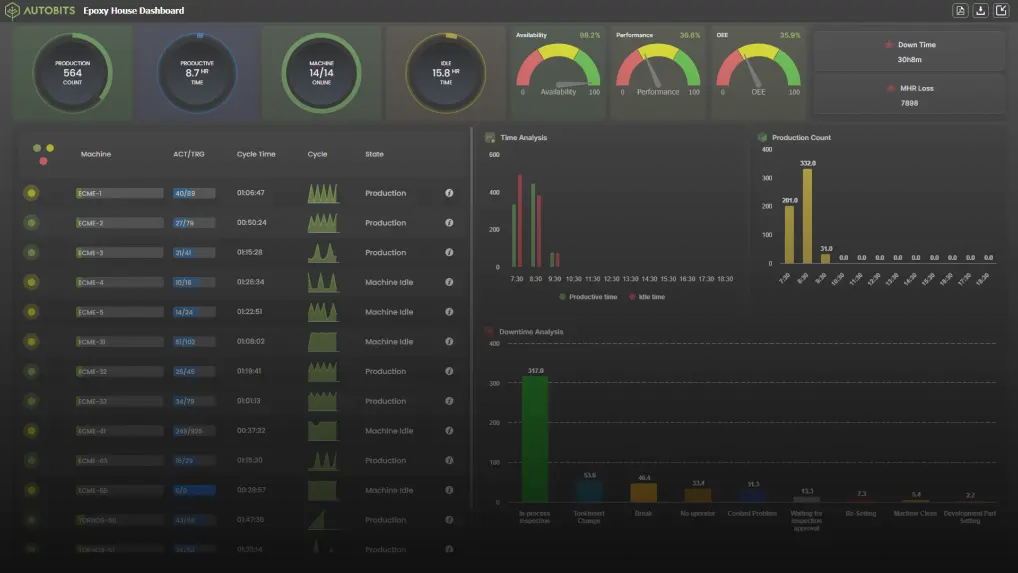
With Autobits CNC Machine Monitoring, all these insights become visible on a single dashboard, enabling data-driven decision-making.
In short, CNC controllers are the brains of machining, while CNC monitoring software acts as the eyes of the factory, ensuring that every machine runs at peak productivity.
FAQs on CNC Controllers
What is a CNC controller?
A CNC controller is the central unit of a CNC machine that interprets program instructions (G-code/M-code) and sends signals to motors and actuators for precise machining operations.
How does a CNC controller work?
It reads coded instructions, processes them in the Machine Control Unit (MCU), and directs machine movements. Feedback sensors ensure accuracy through closed-loop control.
What are the types of CNC controllers?
- Point-to-Point (PTP) Control
- Straight-Line (Linear) Control
- Contour (Continuous Path) Control
- Multi-Axis Controllers
What are the top CNC controller brands in the world?
Some leading brands are FANUC, Siemens, Mitsubishi, Heidenhain, Mazak, Haas, Fagor, NUM, Okuma, and HuazhongCNC.
Which CNC controller is best for beginners?
Haas NGC, and Mazak MAZATROL are popular for beginners and training due to their simple, user-friendly interfaces.
What industries use CNC controllers?
They are widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, mould & die making, heavy machinery, and general manufacturing.
What is the difference between CNC and PLC controllers?
- A CNC controller controls motion and machining operations.
- A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) controls logic and sequencing in industrial automation.
How much does a CNC controller cost?
Prices vary widely:
- Entry-level: $2,000–$5,000
- Mid-range: $10,000–$25,000
- High-end industrial: $50,000+
- (Source: Machine Tool Market Insights, 2024)
Can CNC controllers be upgraded?
Yes. Many brands, such as FANUC and Siemens, allow hardware/software upgrades to support new features, axes, and automation capabilities.
What is the future of CNC controllers?
Future controllers will focus on AI-driven automation, digital twins, adaptive machining, cloud integration, and sustainability for more intelligent, greener factories.
Key Takeaways
- A CNC controller is the brain of every CNC machine, converting digital code into precise machining actions.
- The global CNC controller market is growing steadily and is projected to reach USD 4.8 billion by 2028.
- Top CNC controller brands include FANUC, Siemens, Mitsubishi, Heidenhain, Mazak, Haas, Fagor, NUM, Okuma, and HuazhongCNC.
- FANUC and Siemens dominate globally, holding nearly 45% combined market share.
- Choosing the right controller depends on reliability, ease of use, compatibility, automation features, and after-sales support.
- Future CNC controllers will feature AI, IoT, digital twins, adaptive machining, and enhanced cybersecurity.
- Controllers manage machine-level precision, but monitoring software is essential for factory-level efficiency and OEE tracking.
- Combining a reliable CNC controller with Autobits CNC Machine Monitoring ensures maximum productivity, efficiency, and Industry 4.0 readiness.