Introduction
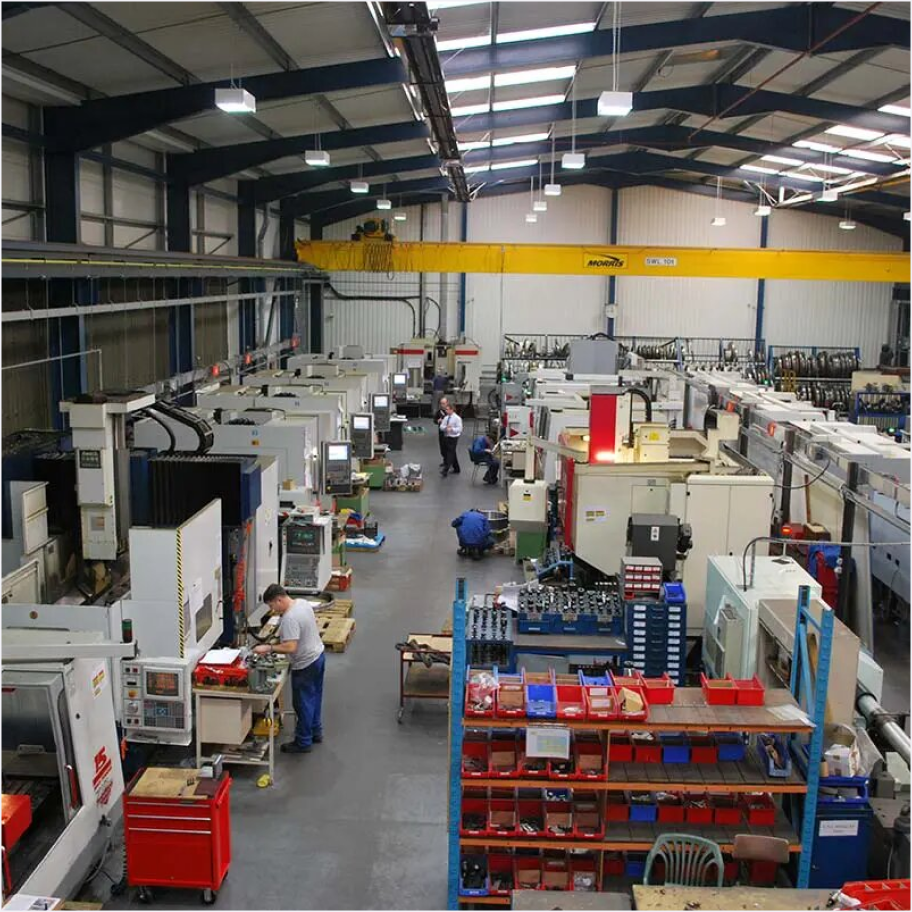
Understanding Two-Way Data Communication
Data Collection:
Data Transmission:
Data Processing:
Benefits of Two-Way Data Communication
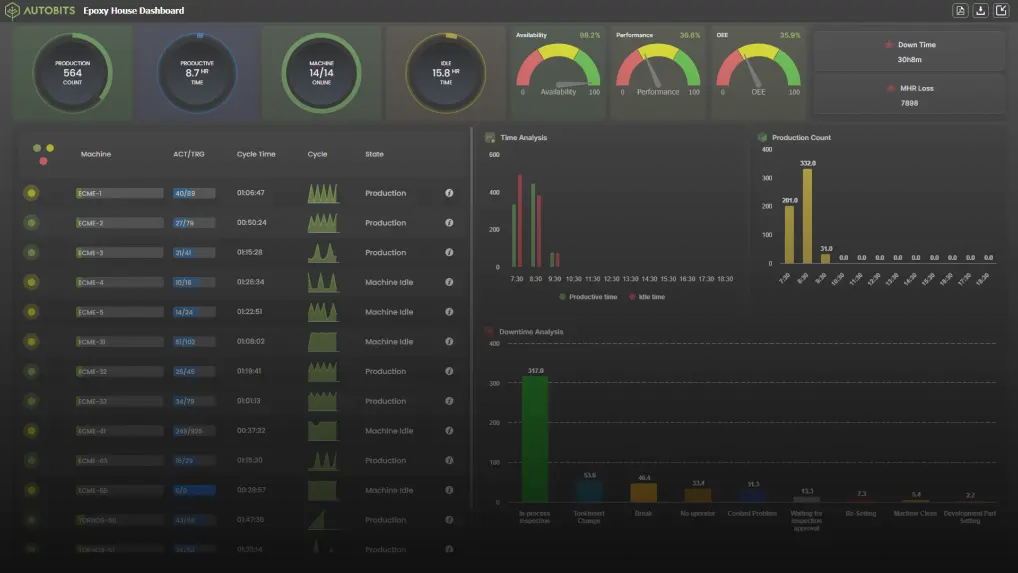
Enhanced Monitoring and Control:
Improved Decision-Making:
Increased Productivity:
Cost Savings:
Security Features:
Data Encryption:
Authentication and Access Control:
Secure Communication Channels:
Comparison Table: Edge vs. Cloud Processing
Aspect | Edge Processing | Cloud Processing |
Latency | Lower latency due to local data processing | Higher latency due to data transmission to the cloud |
Bandwidth | Reduced bandwidth usage | Higher bandwidth usage |
Security | Enhanced security by keeping data local | Increased exposure due to data transmission |
Scalability | Limited by the edge device’s capabilities | High scalability for large-scale data storage |
Benefits of Two-Way Data Communication:
Benefit | Description |
Enhanced Monitoring | Real-time monitoring of machine performance from anywhere using mobile apps. |
Improved Decision-Making | Instant insights into operational performance allow for quicker and more informed decisions. |
Increased Productivity | Optimal machine performance and quick responses to alerts and notifications, minimizing disruptions. |
Cost Savings | Proactive monitoring and predictive maintenance reduce downtime and maintenance costs. |
Data Encryption | Secure encryption of data to prevent unauthorized access. |
Authentication & Access | Multi-factor authentication and role-based access control for enhanced security. |
Secure Communication | Use of secure protocols like MQTT and HTTPS to protect data transmission. |