In today’s digital world, virtual machines (VMs) play a significant role in how companies manage their IT infrastructure. From small startups to large enterprises, most organizations use virtual machines to save costs, improve flexibility, and simplify operations. But as the number of VMs increases, ensuring that each one performs smoothly and efficiently becomes a real challenge. This is where Virtual Machine Monitoring becomes essential.
In this blog, you will learn everything about Virtual Machine Monitoring, including what it is, how it works, what metrics it tracks, and why it is essential for modern IT systems. You will also understand the challenges that come with monitoring virtual environments, along with proven best practices and upcoming trends shaping the future of monitoring.
By the end of this guide, you will have a clear and complete understanding of how to monitor virtual machines effectively, detect performance issues early, and keep your systems stable and optimized. Whether you are an IT professional, a system administrator, or someone exploring virtualization for the first time, this guide will help you gain practical and detailed knowledge on the subject.

What is Virtual Machine Monitoring?
Virtual Machine Monitoring is the process of observing, tracking, and analyzing the performance of virtual machines to ensure they run smoothly and efficiently. It helps IT teams understand how each VM is using system resources such as CPU, memory, disk, and network. By continuously monitoring these elements, teams can identify issues early, avoid downtime, and make better decisions about resource allocation.
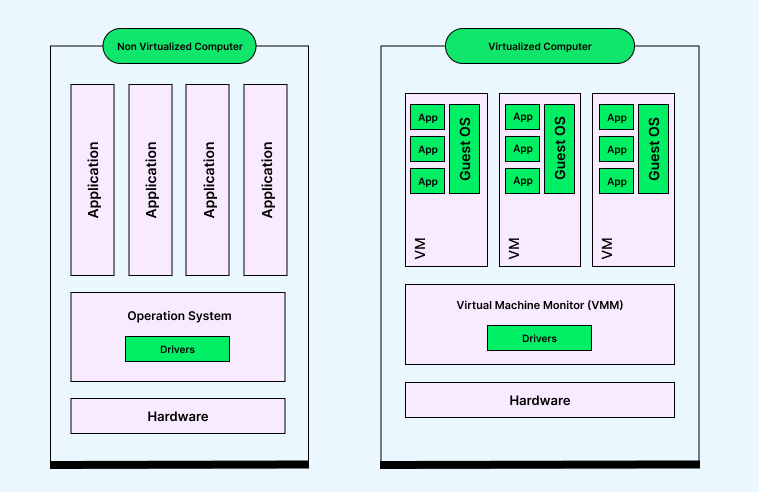
A virtual machine (VM) is a software-based computer that runs on a physical host system. It allows multiple operating systems to run independently on the same hardware. While this improves flexibility and saves cost, it also adds complexity. Since many VMs share the same physical resources, one slow or overloaded VM can affect others on the same host. This is why VM Monitoring is so important. It helps maintain balance, stability, and performance across all virtual environments.
In simple terms, Virtual Machine Monitoring acts like a health check system for your virtual infrastructure. It constantly checks how each VM is performing, reports irregularities, and alerts administrators when something goes wrong. This makes it easier to keep systems reliable, secure, and optimized for daily operations.
Read: Why Your Factory Needs Paperless Manufacturing Software
How Virtual Machine Monitoring Works
Virtual Machine Monitoring works by continuously collecting performance data from different layers of the virtual environment. This includes the host system, hypervisor, and each virtual machine running on it. The goal is to get a complete picture of how the system is performing, identify resource bottlenecks, and detect any unusual behavior before it causes problems.
Data Collection
Monitoring tools gather real-time data using two primary methods: agent-based and agentless monitoring.
- Agent-based monitoring installs a small program, called an agent, inside each virtual machine to collect performance metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network activity.
- Agentless monitoring uses APIs or management interfaces of the hypervisor (like VMware vCenter or Microsoft Hyper-V) to collect data without installing anything inside the VM.
Data Analysis
Once the data is collected, it is analyzed to identify patterns and performance trends. This analysis helps administrators understand which virtual machines are overusing or underusing resources. Modern tools also apply AI and machine learning to detect anomalies automatically and suggest optimizations.
Visualization and Reporting
Monitoring platforms present the collected data through dashboards and visual reports. These dashboards help teams quickly spot issues like high CPU usage or low memory availability. Reports can be scheduled daily, weekly, or monthly to review system health and performance trends.
Alerts and Notifications
If the monitoring system detects a problem, such as a sudden CPU spike or low storage, it automatically sends alerts via email, SMS, or system notifications. This helps IT teams respond quickly before users experience downtime or slow performance.
Continuous Optimization
Virtual Machine Monitoring is not just about fixing issues. It also helps in long-term planning. By studying the data over time, teams can make better decisions about scaling infrastructure, balancing workloads, and managing costs effectively.
Key Metrics Tracked in Virtual Machine Monitoring
Monitoring virtual machines effectively requires tracking the right performance metrics. These metrics reveal how well your system resources are being used and help detect problems before they affect users or business operations. Below are the most critical metrics every IT team should monitor.
CPU Usage
CPU usage shows how much processing power a virtual machine is using. High CPU usage for a long time may indicate that the VM is overloaded or that applications inside it need optimization. Monitoring CPU usage helps prevent performance drops and ensures the system runs efficiently.
Memory Utilization
Memory (RAM) monitoring helps track how much memory each VM consumes. If a VM constantly uses too much memory, it can slow down other VMs on the same host. Keeping an eye on memory utilization ensures balanced resource distribution and smooth application performance.
Disk I/O (Input and Output)
Disk I/O measures how fast data is being read from or written to the storage system. High I/O wait times often cause system lag or application delays. Monitoring disk performance helps identify storage bottlenecks and maintain data flow between the host and the VMs.
Storage Capacity
Running out of disk space can cause system errors or even data loss. Tracking available storage capacity helps administrators plan upgrades or cleanup activities before space becomes critical.
Network Usage
Network monitoring measures traffic in and out of the virtual machine. It helps detect slow data transfers, high latency, or possible network congestion. Monitoring this metric also helps identify security threats like unusual outbound traffic.
Uptime and Availability
Uptime measures how long a VM stays active without interruption. Monitoring availability ensures business continuity and helps track service level agreements (SLAs).
Application Performance
Some tools also monitor applications running inside VMs to check their response times and error rates. This deeper insight helps ensure that not only the virtual infrastructure but also the business-critical applications are working at their best.
Resource Contention
In shared environments, multiple VMs compete for CPU, memory, and storage. Monitoring resource contention helps identify which VMs are consuming more than their fair share so that workloads can be appropriately balanced.
Benefits of Virtual Machine Monitoring
Virtual Machine Monitoring offers several practical advantages for businesses and IT teams. It helps improve performance, prevent issues, and make better decisions about how resources are used. Below are the key benefits that make VM monitoring an essential part of modern IT management.
Prevents Downtime and System Failures
Regular monitoring helps detect issues like high CPU usage, memory leaks, or storage shortages before they cause system crashes. By receiving alerts early, IT teams can take preventive action and keep systems running smoothly without unplanned downtime.
Improves Performance and User Experience
Monitoring ensures that virtual machines and applications perform at their best. When bottlenecks or slow responses are detected, teams can quickly optimize resource allocation or adjust configurations, resulting in faster and more reliable systems.
Optimizes Resource Utilization
Virtual environments often suffer from over-provisioning or underutilization of resources. VM monitoring provides visibility into actual resource usage so that administrators can adjust CPU, memory, and disk allocations based on real needs. This helps avoid waste and improves overall efficiency.
Enhances Capacity Planning
Monitoring data helps IT teams understand usage trends over time. With these insights, they can plan for future capacity needs, ensuring that the infrastructure scales correctly as the business grows.
Strengthens Security and Compliance
VM monitoring can also help identify unusual activities such as unexpected network traffic or resource spikes, which might indicate a potential security threat. Monitoring logs and audit data also helps organizations maintain compliance with IT policies and industry standards.
Simplifies Troubleshooting
When something goes wrong, detailed performance data helps quickly identify the root cause of the issue. This reduces downtime and ensures faster recovery from incidents.
Supports Cost Optimization
By highlighting idle or underused VMs, monitoring tools allow organizations to reduce unnecessary workloads and save on hardware, software, and cloud costs.

Challenges in Virtual Machine Monitoring
While Virtual Machine Monitoring brings many benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Virtual environments are complex, and without the right strategy or tools, it can be not easy to maintain accurate visibility and control. Below are the most common challenges that IT teams face when monitoring virtual machines.
VM Sprawl
VM sprawl happens when too many virtual machines are created without proper tracking or management. Over time, unused or forgotten VMs can waste system resources and make monitoring more complicated. Managing sprawl requires clear policies and continuous review of active virtual machines.
Monitoring Overhead
Monitoring tools themselves consume system resources. If not configured properly, they can add extra load to the host or VMs, affecting performance. Balancing detailed data collection with minimal resource usage is always a challenge.
Identifying Performance Bottlenecks
Since multiple VMs share the same physical resources, finding the root cause of performance issues can be tricky. A slowdown in one VM might actually be caused by another VM or even by the host itself. Effective monitoring requires correlation between host-level and VM-level data to identify real bottlenecks.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Many organizations use a mix of on-premises servers, private clouds, and public clouds. Monitoring across these different environments requires tools that can integrate all performance data into a single view. Without unified visibility, issues may go unnoticed.
Data Overload
Modern monitoring tools collect large amounts of data every second. Without proper filtering or analytics, teams can get overwhelmed by too many metrics and alerts. Intelligent dashboards and automation help focus attention only on critical issues.
Integration with Other Systems
Organizations often use multiple tools for network, application, and security monitoring. Integrating VM monitoring data with these systems can be complex, but it is essential for a complete view of IT health.
Lack of Skilled Staff
Virtualization and monitoring technologies evolve quickly. Without trained professionals, it becomes hard to interpret the data, tune the system, and take timely actions based on monitoring results.
Types of Virtual Machine Monitoring Techniques
Different organizations use different methods to monitor their virtual machines based on infrastructure type, scale, and technical needs. Each technique has its own advantages and limitations. Understanding these methods helps you choose the most suitable approach for your setup.
Agent-Based Monitoring
In this technique, a small software component called an agent is installed inside each virtual machine. The agent collects detailed information such as CPU load, memory usage, disk I/O, and network activity.
Advantages:
- Provides deep visibility into the VM and applications
- Can track process-level data and user activities
- Supports real-time alerts for performance issues
Limitations:
- Consumes system resources
- Requires installation and updates on every VM
- Not ideal for large-scale environments with hundreds of VMs
Agentless Monitoring
Agentless monitoring does not require installing any software inside the virtual machines. Instead, it uses APIs or hypervisor management interfaces such as VMware vCenter, Microsoft Hyper-V Manager, or KVM to collect performance data.
Advantages:
- Easier to set up and maintain
- Uses fewer system resources
- Provides centralized visibility across multiple VMs
Limitations:
- Offers less detailed data compared to agent-based methods
- May have limited customization depending on the hypervisor
Cloud-Native Monitoring
Cloud-native monitoring is used when VMs are hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. These cloud providers offer built-in monitoring tools such as CloudWatch or Azure Monitor that provide detailed metrics, logs, and alerts.
Advantages:
- Integrates directly with the cloud infrastructure
- Provides real-time insights with minimal setup
- Scales easily with cloud resources
Limitations:
- Limited to the provider’s ecosystem
- May require additional tools for hybrid or multi-cloud visibility
API-Based Monitoring
API-based monitoring uses APIs from hypervisors, operating systems, or management tools to pull performance data. It is often used for integrating monitoring data with other platforms or for creating custom dashboards.
Advantages:
- Highly flexible and customizable
- Enables integration with third-party systems
- Supports automation and advanced analytics
Limitations:
- Requires technical expertise to configure and manage APIs
- May have limited data access depending on API permissions
Comparison Table: Monitoring Techniques
| Monitoring Technique | Data Depth | Setup Complexity | Resource Usage | Scalability | Ideal For |
| Agent-Based | Very High | High | Medium to High | Moderate | Detailed performance tracking |
| Agentless | Moderate | Low | Low | High | Quick and centralized monitoring |
| Cloud-Native | High | Low | Low | Very High | Cloud-based environments |
| API-Based | Variable (customizable) | Moderate | Low | High | Integration and automation setups |
Best Practices for Effective VM Monitoring
Monitoring virtual machines is not just about collecting data. It is about understanding data and using it to improve system reliability, performance, and cost efficiency. The following best practices help ensure that your VM monitoring strategy is both accurate and effective.
Set Baseline Performance Metrics
Start by defining what normal performance looks like for your virtual machines. Baseline metrics for CPU, memory, disk, and network usage make it easier to identify when something is wrong. Over time, these baselines help track performance trends and support better capacity planning.
Monitor Both Host and Guest Layers
It is essential to monitor not only the virtual machines but also the host systems that run them. Problems at the host level, such as resource shortages or hardware issues, can affect all VMs. Monitoring both layers gives a complete picture of system health.
Use Unified Dashboards
A centralized dashboard allows administrators to view all VM metrics in one place. This makes it easier to identify issues, compare performance, and make faster decisions. Dashboards with color-coded alerts or charts simplify complex data for quick analysis.
Enable Alerts and Thresholds
Set up alerts for critical conditions such as high CPU usage, low memory, or slow storage. Threshold-based alerts help IT teams respond quickly and prevent downtime. Use smart alerting to avoid false alarms or unnecessary notifications.
Automate Reporting
Automated reports give regular updates on performance, uptime, and resource utilization. These reports help track long-term performance trends, spot recurring issues, and improve decision-making.
Regularly Review and Update Monitoring Rules
As infrastructure changes, monitoring rules and thresholds must also evolve. Review them regularly to ensure that your system reflects current workloads and business needs.
Integrate with Other IT Systems
Combine VM monitoring data with network, application, and security monitoring tools. This integration gives a unified view of the entire IT environment and helps detect issues that might affect multiple layers.
Focus on Capacity and Cost Optimization
Use monitoring data to identify underused or over-provisioned resources. Deleting idle VMs or resizing overpowered ones can help save significant costs while maintaining performance.
Leverage Predictive Analytics and AI
Modern monitoring tools use AI to detect unusual behavior and predict potential problems before they occur. Implementing AI-driven analytics helps reduce manual work and keeps systems running proactively.
Ensure Data Security and Compliance
Make sure your monitoring setup follows organizational security policies. Access to monitoring data should be restricted to authorized users, and logs should be stored appropriately for compliance and audit requirements.

Role of AI and Automation in Modern VM Monitoring
As virtual environments grow larger and more complex, manual monitoring becomes difficult and time-consuming. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation now play a significant role in improving the accuracy, speed, and efficiency of Virtual Machine Monitoring. They help IT teams move from a reactive approach to a proactive one, where issues are predicted and prevented before they affect performance.
Intelligent Anomaly Detection
AI-powered monitoring tools continuously analyze large volumes of performance data to identify unusual behavior or patterns. For example, if a virtual machine’s CPU usage suddenly spikes without a reason, AI systems can detect it instantly and alert the administrator. This helps catch issues early, even before they turn into system failures.
Predictive Analytics
With predictive analytics, AI uses past data to forecast future trends. It can predict when a VM might run out of storage, when performance will drop, or when a component is likely to fail. This allows IT teams to plan maintenance activities and avoid downtime.
Automated Alerts and Remediation
Automation helps streamline responses to common issues. Instead of waiting for manual intervention, the system can take predefined actions automatically, such as restarting a service, allocating more memory, or shifting workloads to another host. This reduces downtime and minimizes the need for human effort.
Resource Optimization
AI helps optimize resource usage by analyzing workloads and recommending changes in real time. It can identify underutilized resources and suggest consolidation or resizing of VMs to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Smarter Decision-Making
AI combines performance data from different layers, such as the host, VM, and application. By analyzing all of it together, it provides deeper insights into system health, making it easier for IT managers to make smarter and faster decisions.
Integration with AIOps Platforms
AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) brings together machine learning and automation to enhance monitoring and management processes. When VM monitoring is integrated with AIOps, it becomes more intelligent, adaptive, and self-healing, helping organizations maintain uptime with minimal human input.
Reduced Human Errors
Automation eliminates repetitive manual tasks like log checking or data correlation, reducing the risk of mistakes. This ensures consistency, accuracy, and faster response times in managing virtual infrastructures.
Future of Virtual Machine Monitoring
The world of virtualization is changing rapidly, and so is the way we monitor it. As cloud computing, hybrid infrastructures, and container technologies continue to evolve, Virtual Machine Monitoring is also moving toward more innovative, more automated, and more integrated systems. The future of VM monitoring will focus on predictive intelligence, unified visibility, and complete observability.
Shift Toward Observability
Traditional monitoring focuses on metrics, logs, and alerts, while observability digs deeper into system behavior. Observability tools help understand why something went wrong, not just what went wrong. Future monitoring systems will combine both approaches to give IT teams more insight and control over performance issues.
Unified Monitoring for Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Enterprises now use a mix of on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud systems. Future monitoring tools will provide unified visibility across all these environments. This will help teams track performance consistently, no matter where their virtual machines are running.
Increased Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI will continue to make monitoring smarter by automating the detection, analysis, and resolution of problems. Machine learning models will use historical performance data to predict future issues, suggest improvements, and optimize resource usage automatically.
Deeper Integration with Containers and Kubernetes
As many organizations move toward containerization, future VM monitoring systems will need to handle both virtual machines and containers together. Unified dashboards will help track performance at every layer, from physical hardware to containers running on top of VMs.
Cloud-Native and Edge Monitoring Growth
With the rise of cloud-native and edge computing, monitoring will expand beyond data centers. Future systems will need to handle distributed environments where VMs run at the network edge, closer to users or IoT devices.
Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient computing is becoming a global priority. Future monitoring tools will track power consumption and resource efficiency to help organizations lower energy costs and reduce their environmental impact.
Self-Healing Virtual Environments
Automation and AI will lead to self-healing systems that can detect, diagnose, and fix issues automatically. This approach will reduce downtime and human intervention, allowing IT teams to focus on innovation rather than maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Virtual Machine Monitoring?
Virtual Machine Monitoring is the process of tracking and analyzing the performance, health, and resource usage of virtual machines. It helps system administrators detect issues, optimize workloads, and ensure smooth operation of virtualized environments.
Why is VM Monitoring important?
VM Monitoring ensures that virtual machines perform efficiently without wasting resources. It helps prevent downtime, improves performance, and allows early detection of potential problems before they affect end users.
What metrics are monitored in Virtual Machines?
Key VM metrics include CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, network traffic, uptime, and process health. Monitoring these metrics helps identify performance bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
How does Virtual Machine Monitoring work?
Monitoring software collects real-time data from hypervisors, virtual machines, and operating systems. It then analyzes this data to provide alerts, reports, and insights about performance, availability, and health.
What is the difference between VM monitoring and observability?
VM monitoring focuses on tracking known metrics like CPU, memory, and uptime. Observability goes a step further by helping identify unknown issues and understanding why they occurred using logs, traces, and advanced analytics.
Can VM Monitoring tools predict issues before they happen?
Yes. Modern tools use AI and machine learning to analyze historical data and identify unusual patterns. This predictive approach helps prevent failures and maintain consistent performance.
How often should you monitor virtual machines?
Continuous, real-time monitoring is ideal. It ensures instant alerts when performance issues arise, helping teams respond quickly and minimize downtime.
What is the best way to monitor multiple virtual machines?
Use a centralized monitoring dashboard that provides visibility across all virtual machines. This helps track performance metrics, manage alerts, and generate reports from a single interface.
Does VM Monitoring support both on-premise and cloud environments?
Yes. Most advanced monitoring systems can monitor virtual machines running on on-premises servers, private clouds, and public cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
What challenges are faced in Virtual Machine Monitoring?
Common challenges include data overload, limited visibility across hybrid systems, false alerts, and scalability issues. The right tool can overcome these with automation, AI insights, and unified dashboards.
How is VM monitoring different from server monitoring?
Server monitoring focuses on physical hardware performance, while VM monitoring deals with virtualized environments running on that hardware. VM monitoring tracks virtual CPU, memory, and storage assigned to each virtual machine.
Are there open-source tools for Virtual Machine Monitoring?
Yes. Popular open-source tools include Prometheus, Zabbix, and Nagios. These tools are customizable, cost-effective, and widely used in IT infrastructure monitoring.
What is predictive VM Monitoring?
Predictive VM Monitoring uses AI algorithms to forecast potential failures or resource shortages by analyzing historical performance data and trends.
Can VM Monitoring improve cost efficiency?
Yes. By identifying underutilized resources and optimizing workloads, monitoring tools help reduce unnecessary expenses and improve return on infrastructure investment.
What is the future of Virtual Machine Monitoring?
The future will bring more automation, AI-driven insights, and unified observability across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Systems will become self-healing, energy-efficient, and capable of handling both VMs and containers seamlessly.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Virtual Machine Monitoring is no longer just a technical necessity; it has become a strategic part of managing modern IT infrastructure. As organizations depend more on virtual environments, effective monitoring ensures that every virtual machine performs at its best while maintaining stability, security, and efficiency.
From understanding the basics of how VM monitoring works to exploring its future trends like AI-powered automation and observability, this guide aims to give you a complete picture of the topic. Whether you are a beginner learning how virtual machines are tracked or an experienced IT professional optimizing hybrid systems, the principles remain the same: visibility, control, and proactive management are key.
Key Takeaways
- Virtual Machine Monitoring helps track performance, uptime, and resource usage in virtualized systems.
- Continuous monitoring helps detect problems early, reducing downtime and maintaining productivity.
- Advanced tools use AI and predictive analytics to forecast performance issues before they happen.
- Integration with cloud, container, and edge systems is the future of monitoring.
- The proper VM monitoring setup improves both performance and cost efficiency while ensuring scalability.
By applying these insights, businesses and IT teams can make smarter infrastructure decisions, strengthen reliability, and ensure their systems stay ready for tomorrow’s challenges.