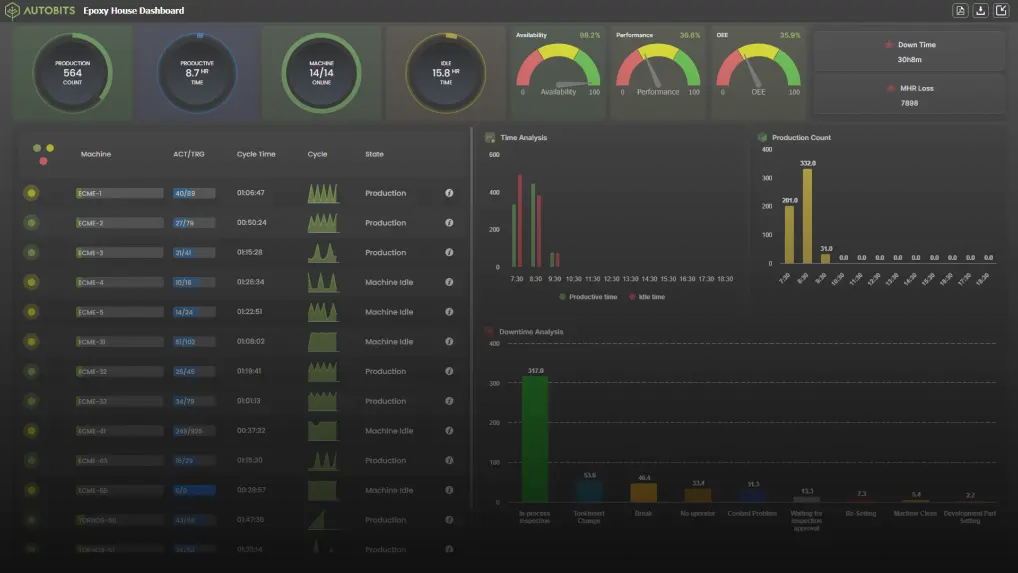
After having a quick start on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), let us also have look at TPM.
After having a quick start on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), let us also have look at TPM.
A universal approach for equipment maintenance that optimizes the production process can be termed as Total Production Maintenance (TPM).
Operational efficiency of machines can maximized by preventive and proactive maintenance approach of TPM. TPM clears the hurdle between production and maintenance management by facilitating the managers and operators to help them maintain their equipments.
TPM program thus helps to increase the involvement of floor workers by creating an atmosphere for shared responsibility of resources and equipments. This can be very powerful in improving the productivity by increasing up time and reducing cycle time.
TPM typically emphasizes on:
- Zero defects
- Zero stoppages
- Zero breakdowns
- Zero accidents
Conventional TPM
Introduced in 1960s, the core of conventional TPM model lies within the following 5 foundation phrases and 8 pillars.
Foundation Phrases
The foundation phrases of TPM consists of what is popularly known as ‘5s‘. It builds a working atmosphere which must be neat and well-organized. The 5s are:
- Seiri / Sort – Discarding the objects which are not needed in the work area
- Seiton / Set in Order – Arranging remaining objects in an efficient manner.
- Seiso / Shine – Cleaning and inspecting the work area thoroughly.
- Seikestu / Standardize – Building standards for properly performing previous three steps
- Shitsuke / Sustain – Interaction within employees to ensure that standards are regularly incorporated.
In a clean and well-organized working environment, where machines are properly arranged, it becomes easier to find any tool or parts. Identifying layback such as fluid leaks, hairline cracks, fluid leads during production becomes easy. Thus creating 5s foundation makes the working process easy and flawless.
Pillars of TPM
The eights pillars or activities of TPM focus on preventive and proactive measures to improve machine reliability.
- Autonomous Maintenance
- Planned Maintenance
- Quality Maintenance
- Focused Improvement
- Early Equipment Management
- Training and Education
- Safety, Health, Environment
- TPM in Administration