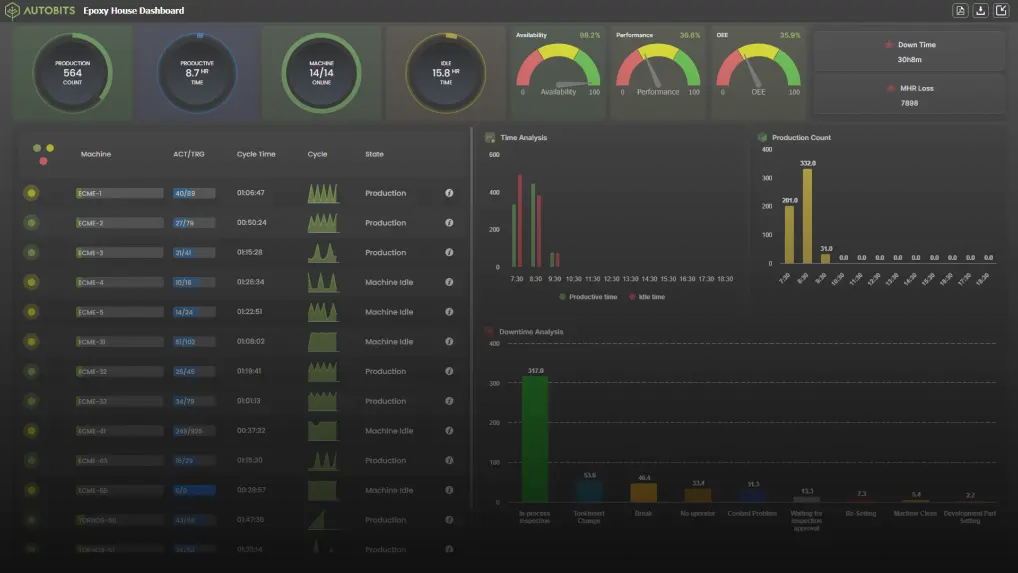
Machine monitoring is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance the performance and productivity of CNC machines. By collecting real-time data from machine tools, monitoring systems help operators detect issues quickly, optimize production, and reduce costly downtime. However, for machine monitoring software to function effectively, it relies on specific features within the CNC controller.
In this blog, you’ll learn:
- What makes a CNC controller compatible with machine monitoring software?
- The importance of protocols like MTConnect and OPC UA for data communication.
- Which CNC controllers support Ethernet-based communication for seamless integration?
- What to do if your CNC controller requires add-on hardware for monitoring.
- How to handle controllers that do not provide digital or detailed data.
- The key features to look for in a CNC controller for effective machine monitoring.
- How to check if your CNC controller is compatible.
- Mistakes manufacturers make when selecting controllers for monitoring.
- What to do if your controller is outdated.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have a complete understanding of how to choose the right CNC controller for your monitoring needs and optimize your machine monitoring system.
Compatible CNC Controllers for Machine Monitoring
A compatible CNC controller is one that can support the protocols and data formats necessary for effective machine monitoring. The most crucial factor for compatibility is connectivity. The controller must be able to send real-time machine data (such as operational status, cycle times, alarms, and production counts) to the monitoring software.
Two primary communication protocols for machine monitoring are MTConnect and OPC UA. MTConnect is an open-source standard designed for easy data exchange, while OPC UA offers a more comprehensive solution that allows both read and write access to machine control data. CNC controllers that support these protocols make it easy for machine monitoring software to collect and interpret data, providing valuable insights into machine performance.

CNC Controllers with Ethernet-Based Communication
Ethernet connectivity is essential for machine monitoring as it enables real-time data transfer over a network. This makes it easy for monitoring software to access machine data remotely. CNC controllers with built-in Ethernet support are the best candidates for machine monitoring integration.
Examples of CNC controllers that support Ethernet-based communication include:
- FANUC Controllers: FANUC controllers such as the 30i, 31i, and 32i series have Ethernet ports and support the FANUC FOCAS communication library. This allows monitoring systems to access over 100 data points, including spindle load, alarm status, and part counts.
- Siemens Sinumerik: Siemens Sinumerik 840D and Sinumerik ONE controllers offer Ethernet/IP and PROFINET protocols, which allow them to connect with monitoring software seamlessly. These controllers also have an embedded OPC UA server for secure data transmission.
- Haas Next-Generation Control (NGC): Haas controllers with NGC come equipped with an embedded MTConnect agent that allows monitoring software to collect real-time data through Ethernet.
These controllers provide open-standard communication and are highly compatible with most machine monitoring systems, making them easy to integrate into your workflow.
CNC Controllers That Require Add-On Hardware
Not all CNC controllers come with built-in Ethernet or modern communication protocols. For legacy machines or specialized models, you may need additional hardware to enable machine monitoring.
For example:
- Mitsubishi Electric: Older Mitsubishi controllers, like the MELDAS series, may lack Ethernet connectivity. To enable machine monitoring, additional software (like the NC Machine Tool Connector) or IoT gateways can be used to connect the machine to the network and provide data via MTConnect or OPC UA.
- Mazak: Mazak machines that do not support MTConnect can be equipped with the SmartBox gateway, which converts machine signals into MTConnect-compatible data streams, allowing integration with machine monitoring systems.
These add-on solutions make it possible to bring older or specialized CNC machines into the machine monitoring system, ensuring you can still collect valuable data.
CNC Controllers That Don’t Provide Digital Data
Some older CNC controllers or specialized models may only provide basic signals, like machine on/off status, and do not transmit detailed digital data. These controllers limit the ability to gather in-depth operational insights but may still be helpful for simple monitoring tasks, such as detecting machine state or alarms.
For example:
- CNC Routers, EDMs, Plasma Cutters: These types of machines often use custom or proprietary controllers that don’t support advanced data protocols like MTConnect or OPC UA. Monitoring systems for these machines typically rely on simple I/O signals to track machine state, such as cycle start/stop or basic alarms.
- Legacy CNC Machines: Older machines may only provide basic signals to indicate whether they are running or stopped. They may not offer more detailed data like cycle times, operational status, or production counts.
While these machines can be monitored at a basic level, adding external sensors or retrofit solutions such as IoT gateways can improve data collection capabilities, providing richer data for analysis.
Key Features Required for Modern CNC Monitoring
To effectively monitor machine performance, CNC controllers should include certain features that facilitate communication with monitoring software and allow for comprehensive data collection.
Essential features for modern CNC monitoring include:
- Support for MTConnect or OPC UA: These open communication protocols allow monitoring systems to collect and interpret machine data easily.
- Ethernet Connectivity: Built-in Ethernet ports or wireless options enable seamless data transfer, allowing for remote monitoring without the need for additional hardware.
- Real-Time Data: The ability to stream real-time machine data, such as spindle load, axis positions, cycle times, and alarm statuses, is critical for proactive monitoring and optimization.
- Data Logging and Alerts: Controllers that log operational events and provide automated alerts (such as maintenance reminders or fault notifications) can help prevent downtime and improve machine efficiency.
- Expandability: Controllers should be capable of adding I/O modules or sensors to track specific events like tool changes, door openings, or coolant levels.
These features ensure that your CNC controller is fully equipped to handle the demands of modern machine monitoring systems, providing valuable insights into production performance.
Read: Network Requirement Checklist for CNC Machine Monitoring
How to Check If Your CNC Controller Is Compatible
Before integrating a CNC controller with machine monitoring software, it’s essential to verify its compatibility. Here’s how you can check:
- Review the User Manual: The manual or technical documentation will outline the communication protocols supported by the CNC controller.
- Look for Ethernet Ports: Check if the controller has Ethernet connectivity. Ethernet is essential for remote data access and integration with monitoring systems.
- Verify Protocol Support: Confirm whether the controller supports open protocols like MTConnect or OPC UA. These protocols simplify the data integration process and ensure compatibility with monitoring software.
- Contact the Manufacturer: If you are unsure, reach out to the manufacturer or supplier for more detailed information about the controller’s connectivity features.
By performing these checks, you can easily determine whether your CNC controller is compatible with your machine monitoring system.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting CNC Controllers for Monitoring
Choosing the wrong CNC controller can create difficulties in integrating your machine with a monitoring system. Some common mistakes manufacturers make include:
- Choosing Controllers Without Open Protocol Support: If a controller doesn’t support MTConnect or OPC UA, it will be challenging to integrate with monitoring systems, limiting the effectiveness of your machine monitoring setup.
- Opting for Older Models with Limited Connectivity: Older machines often lack Ethernet ports or modern data protocols, making them more challenging to connect with modern monitoring systems.
- Overlooking Expandability: Failing to consider future needs for additional sensors or I/O modules can limit the controller’s usefulness as production requirements evolve.
By understanding these common pitfalls, you can make an informed decision when selecting a CNC controller for your machine monitoring system.

What to Do if Your CNC Controller Is Outdated
If your CNC controller is outdated or doesn’t support modern monitoring features, you have several options:
- Retrofitting with Gateways: Many legacy CNC machines can be upgraded with IoT gateways or protocol converters. These devices allow your machine to communicate with modern monitoring systems, even if the controller doesn’t natively support open protocols like MTConnect or OPC UA.
- Upgrading the Controller: If your machine is compatible, upgrading to a modern controller with built-in Ethernet and support for open protocols can simplify the integration process and provide long-term benefits.
- Adding Sensors: For machines that don’t provide sufficient data, external sensors or custom interfaces can help capture critical operational data, such as cycle times, machine state, and alarms.
These options ensure that your machines stay connected and optimized for real-time monitoring, even if the original controller lacks modern features.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CNC controller for machine monitoring is critical for optimizing production, reducing downtime, and gaining valuable insights into machine performance. Controllers with built-in support for protocols like MTConnect and OPC UA, as well as Ethernet connectivity, are the most compatible with modern machine monitoring systems. If you’re working with legacy machines, retrofitting them with gateways or upgrading to newer controllers can allow you to harness the full potential of machine monitoring.
By carefully evaluating the features and compatibility of your CNC controller, you can ensure smooth integration with your machine monitoring system and improve overall efficiency on the shop floor.
FAQs
What protocols should my CNC controller support for machine monitoring?
Your CNC controller should support MTConnect or OPC UA for seamless integration with machine monitoring software.
Can I monitor my CNC machine if it doesn’t have Ethernet connectivity?
Yes, but you will need to use external hardware like IoT gateways or retrofit solutions to enable connectivity.
How do I check if my CNC controller is compatible with machine monitoring?
Check the user manual, look for Ethernet ports, verify protocol support, and contact the manufacturer for more details.
What if my CNC controller is outdated and doesn’t support modern protocols?
You can retrofit your machine with IoT gateways, upgrade the controller, or add external sensors to enable monitoring.
What are the most common mistakes to avoid when selecting CNC controllers for monitoring?
Avoid selecting controllers without open protocol support, overlooking expandability, or choosing outdated machines with limited connectivity.